Difference Between Wheat Germ and Wheat Bran
Both the wheat germ and the wheat bran are often by-products of milling when the intent is to produce white flour, mainly to improve the flour’s storage qualities or when a finer and smoother texture is needed in cooking and baking. They have carbohydrates, proteins, fiber, vitamins and minerals like phosphorus, magnesium, zinc, and iron. The germ and the bran are removed due to their fat content which tends to oxidize and become rancid on storage. Separated from the endosperm, wheat germ and bran are used mainly as food additives in cooking and baking. They sometimes find their way to the livestock industry, where they are used as animal feeds.
Wheat germ and wheat bran are two different parts of the wheat grain, which is also sometimes called the wheat berry. These two parts, along with the endosperm (surrounding the germ), make up the kernel – or grain of the wheat plant. Wheat germ and wheat bran, and their differences are further discussed in the following.

What is Wheat Germ?
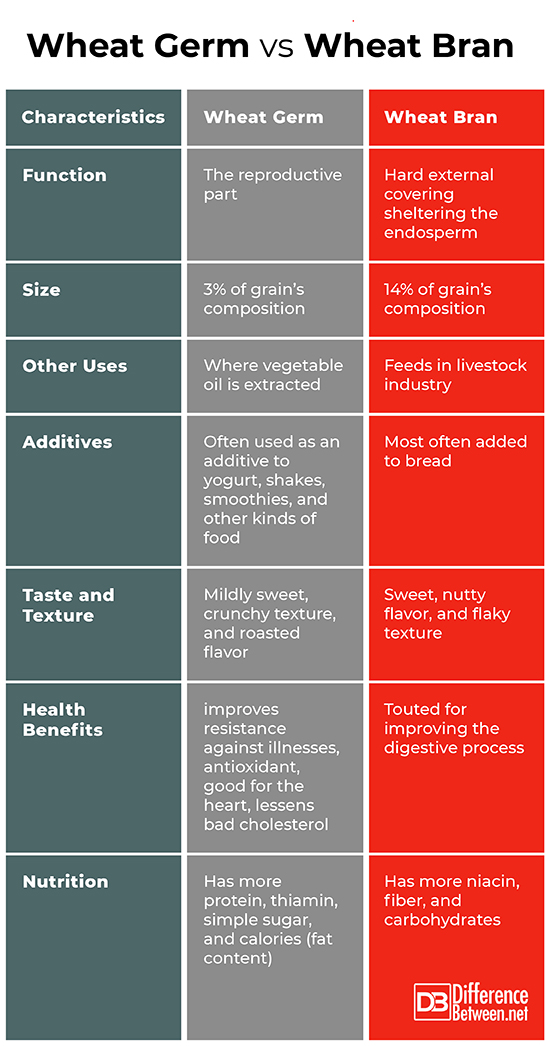
The germ, also called the embryo, is the reproductive part which would eventually germinate and grow if the grain is planted. It is the smallest part, making up only about 3% of the grain’s composition. Although mainly used in the food industry, as by-products of the milling process, the wheat germ, along with the germ of other cereal grains, may be used as a source from which vegetable oil is extracted. Despite its small size, the wheat germ is the most nutrient-dense part of a whole grain. It is richer in protein and packed with important nutrients including vitamin E, vitamin B1 (thiamin), minerals, as well as essential fatty acids and fatty alcohols. In terms of health benefits, the wheat germ can boost immunity due to its vitamin B content. It also promotes cardiovascular health and maintains ideal levels of cholesterol due to its lower fat content than most other types of food that come from plants. The vitamin E also serves as anti-oxidants which help fight free radicals that speed up aging.

What is Wheat Bran?
The bran is the hard, outer covering which serves to protect both the endosperm and the germ. It makes up about 14% of the whole grain’s composition. It promotes proper digestion, making it ideal for those suffering from constipation or loose bowel movement because of its high fiber content. The nutrients it provides include protein, carbohydrates, dietary fiber, thiamine, riboflavin, vitamin B6, potassium, iron, magnesium, and phosphorus. Due to its sweet taste, it is also an ideal additive in baked goods.
Difference between Wheat Germ and Wheat Bran
Function
The germ is the reproductive part which would eventually germinate and grow if the grain is planted. On the other hand, the bran is the tough outer covering which serves to protect both the endosperm and the germ.
Size
The germ is the smallest part, making up only about 3% of the grain’s composition while the bran makes up about 14% of the whole grain’s composition.
Other Uses
The wheat germ, along with the germ of other cereal grains, may be used as a source from which vegetable oil is extracted. The wheat bran, on the other hand, may also be used with other cereal brans as feeds in the livestock industry.
As an Additive
Being high in protein, wheat germ is typically added to smoothies, yogurt, casseroles, protein shakes, and other similar food items. As for wheat bran, due to its sweeter taste, is ideal as an additive in baked goods.
Taste and Texture
The wheat germ tastes nutty and has crunchy texture while the wheat bran is distinct in its sweet taste and flaky texture.
Health Benefits
In terms of health benefits, the wheat germ can boost immunity due to its vitamin B content. It also promotes cardiovascular health and maintains ideal levels of cholesterol due to its lower fat content than most other types of food that come from plants. The vitamin E also serves as anti-oxidants which help fight free radicals that speed up aging. Meanwhile, the wheat bran promotes proper digestion, making it ideal for those suffering from constipation or loose bowel movement because of its high fiber content.
Nutrition
The wheat germ is richer in protein and packed with important nutrients including vitamin E, vitamin B, and fatty alcohols. In comparison, the wheat bran is richer in fiber, three times that of the wheat germ and has more niacin.
Wheat Germ vs Wheat Bran
Summary of Wheat Germ vs Wheat Bran
- Both the wheat germ and the wheat bran are often by-products of milling when the intent is to produce white flour.
- The germ, also called the embryo, is the reproductive part which would eventually germinate and grow if the grain is planted.
- The bran is the hard, outer covering which serves to protect both the endosperm and the germ.
- The wheat germ is smaller than the wheat bran.
- Vegetable may be extracted from wheat germ while wheat bran may be fed to livestock.
- The wheat germ is crunchy and mildly sweet while wheat bran is sweet, nutty, and flaky.
- Wheat bran is mostly added to bread and cereals while wheat germ is a common additive to shakes, smoothies, and other kinds of food.
- The wheat germ has generally more nutritional benefits than the wheat bran.
- Difference Between Hematoma and Melanoma - February 9, 2023
- Difference Between Bruising and Necrosis - February 8, 2023
- Difference Between Brain Hematoma and Brain Hemorrhage - February 8, 2023
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bran#/media/File:WheatBran.jpg
[1]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Crust_of_milk_loaf_with_wheatgerm.jpg
[2]Bewley, Derek J., Michael Black, and Peter Halmer. The Encyclopedia of Seeds: Science, Technology and Uses. London, UK: CAB International, 2006.
[3]Lamb, Robert. How Wheat Works. September 2008. https://science.howstuffworks.com/life/botany/wheat2.htm (accessed July 5, 2019).
[4]Mauseth, James D. Botany: An Introduction to Plant Biology. Jones & Bartlett Publishers, 2014.
