Difference Between Absolutism vs Constitutionalism
What is Absolutism?
Definition of Absolutism:
The term Absolutism finds its roots in the works of famous political philosopher Jean Bodin later Thomas Hobbes built on the arguments of Jean Bodin. His works lead to the formulation of absolutist theory derived from the concept of c. According to this theory, “not only must all states be sovereign (or they are not the states), but sovereignty therein must be unlimited and undivided (or it is no longer sovereignty)” (Hoekstra 1079). In other words, absolutism gives unlimited and uncontrolled power in the hands of monarch in the name of “divine’s right to rule”.
Characteristics of Absolutism:
There are certain characteristics implicated by absolutism:
- The monarch gets the hold of cultural life of people and impose censorship on the expression of arts or any other expression that poses a threat to their rule.
- The king exhibits his pomp and power by luxurious life style. It is also meant to justify that they are “the chosen ones”.
- The sovereign is responsible to look what goes best in the interest of the state as they have the divine right to rule and choose the best for the subject.
- In any absolutist state, crown and aristocracy shared in the benefits of power (Black 39).
Traditionally, absolutism has typically been seen as the triumph of the ‘state’ over society – new bureaucracy, loyal army, centralized royal power (Black 39).
The stress on religion and ideology is a helpful one as it provides a new basis for understanding absolutism in terms of cooperation between crown and aristocracy, rather than in terms of a hostile relationship between ‘state’ and society, in which coercion played an important role and the localities and aristocracy sought to act without reference to the crown (Black 39).
Example of Absolutism:
From fifteenth century to eighteenth century Absolutists states were prevalent in the Europe until their power was dissolved. France, Prussia, Spain, Austria, some areas of central Europe, Russia, Ottoman Empire, some territories of England.
Constitutionalism:
Definition of Constitutionalism:
The conceptual basis of constitutionalism finds its basis from the political theories of John Locke where he questioned the unlimited power of the sovereign. According to his theories, “government can and should be legally limited in its powers, and that its authority or legitimacy depends on its observing these limitations” (Waluchow 1). Constitutionalism constricts the unlimited power of sovereign by regulating the system through constitution.
Thus, Charles Howard McILwain in his famous book Constitutionalism: Ancient and Modern quotes Thomas Paine as, “A constitution is not the act of government, but of people constituting a government, and a government without constitution is a power without right” (MclLwain 4).
Characteristics of Constitutionalism:
Constitutionalism possess certain characteristics some of them are given below:
- Constitutionalism ensures check and balance on the government through a specific set of values, norms and a certain structure.
- The state is governed by the rule of law.
- “Constitutionalism has one essential quality; it is a legal limitation on government; it is the antithesis of the arbitrary rule; it’s opposite is the despotic government; the government of will instead of law” (McILwain 24).
- Sovereign and subject both are bound to submit to authority of law.
Examples of Constitutionalism:
In ancient times, Roman empire is an example of Constitutionalist state. “In Roman empire the word in its Latin form became the technical term for acts of legislation by the emperor, and from Roman law the Church borrowed it to ecclesiastical regulations for the whole Church or for some ecclesiastical province” (McILwain 25). In modern world, innumerable countries operate in accordance with this system.
Similarities between Absolutism and Constitutionalism:
- Both operate for the welfare of state. Both are responsible for the protection of their masses and the state.
- Both run the state by collecting taxes from people either directly or through a proper system of taxation.
Differences between Absolutism and Constitutionalism:
- Absolutism leads to absolutists states where a few rules over the state by “divine right to rule” it often translates into tyranny of majority or of the same aristocratic families whereas I constitutionalism rule of law prevails.
- No one can question unbridled power of the king in absolutism while in constitutionalism power is decentralized by dividing among the institutions.
- In Absolutism, king obtains wealth directly from people while in constitutionalism there is no system of obtaining money directly rather they have to go through a formal procedure to collect finances from nobles.
- Regardless of the situation of peace and war, there is a standing army in absolutist states. But in constitutionalist states, army is only mobilized at the instances of war and chaos.
- Absolutism limits the freedom of the masses by excessive surveillance and censorship while Constitutionalism is responsible for ensuring freedom and liberty of people in the state.
Absolutism Vs Constitutionalism: Comparison
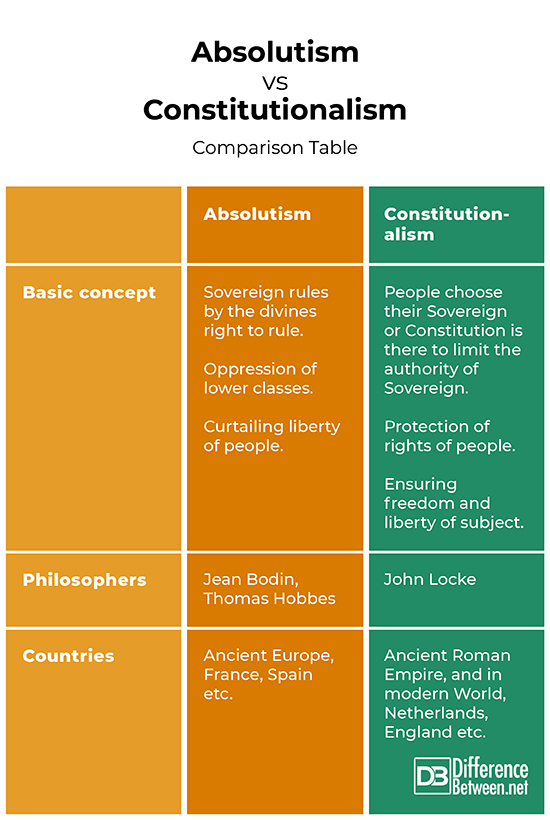
Summary of Absolutism Vs Constitutionalism:
Absolutism and Constitutionalism in Political philosophy account for the system of government.
Both found their roots in fifteenth century where in France a few families were kept in power by the putting forth the argument that they have been chosen by God and hence are superior to others. They exhibit their absolute authority and exploited the lower class until John Locke questioned the idea of infinite power and the concentration of power in a few hands. According to him, there is a limitation to the rights and authority of sovereign. So, constitutionalism divides this power in certain institutions which then operates according to the constitution made by keeping in view the benefits of the people while ensuring their liberty and protection. Constitutionalism provides the basis for “the rule of law” where no one can be above the rule of law.
- Difference Between Court of Law and Court of Justice - August 10, 2019
- Difference Between Labor Day and Memorial Day - July 28, 2019
- Difference Between Whistleblower and Leaker - July 27, 2019
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Black, Jeremy. “Recent Work on European Absolutism.” Teaching History, no. 50, 1988, pp. 39–40. JSTOR, www.jstor.org/stable/43256682.
[1]Hoekstra, Kinch. “Early Modern Absolutism and Constitutionalism.” HeinOnline, 2012, heinonline.org/HOL/LandingPage?handle=hein.journals%2Fcdozo34&div=37&id=&page=&t=1556276346.
[2]McILwain, Charles Howard. “Constitutionalism: Ancient and Modern”, Google Books, Google, 2005, books.google.com.pk/books?hl=en&lr=&id=vNGB2kB6tr0C&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=Political%2BAbsolutism%2BVs%2BConstitutionalism&ots=otpxAFHDEi&sig=M6GTOMlGYrDHSV6ixIl0V3ljezw#v=onepage&q=Political%20Absolutism%20Vs%20Constitutionalism&f=false.
[3]Waluchow, Wil, "Constitutionalism", The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Spring 2018 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.), URL =
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Constitutionalism.jpg
[5]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Louis_ambassador_1663.jpg
