Difference Between Hybrid and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles
Vehicle manufacturing is one of the major industries that have been adapted to meet present day requirements of sustainable development. The key component of sustainability requires the design of environment friendly vehicles.

Conventional vehicles use petroleum as the only source of energy and represent the majority of the existing vehicles today. However, rising petroleum prices and shortage of petroleum have become a major challenge for the vehicle owners. Growing concerns of the limited-supply of fuels are motivating vehicle manufacturers to invest in pollution-free alternate energy vehicles.
Electric vehicles are believed to be the future of alternative energy. They are one of the most promising technologies that hit the automotive industry. Electric vehicles are mainly classified into Hybrid and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles.
What are Hybrid Electric Vehicles?
Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) is a vehicle that no longer depends solely on the internal combustion engine (ICE) to propel the engine, but rather uses an electric motor to propel the vehicle using electricity.
It combines the benefits of both traditional electric vehicles and existing technology to make the best of both the worlds. HEVs are the most practical and energy-efficient alternative to conventional vehicles because they are powered by both ICE and the electric drive system.
However, unlike PHEVs, they are not able to charge the battery from the electricity grid because the power comes from regenerative braking or petrol in the tank.
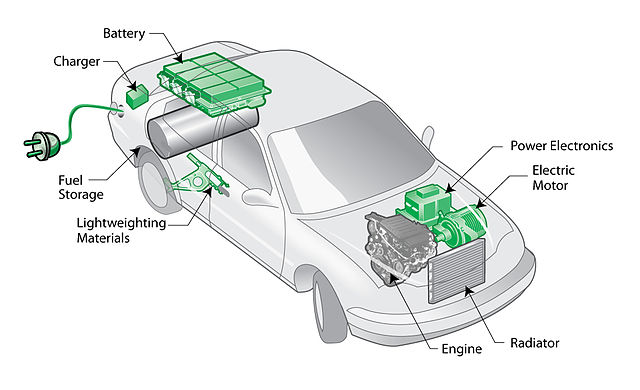
What is Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles?
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles, or PHEVs, are the next generation of hybrid electric vehicles that are fairly new to the scene but are quick to gain traction because of their increased efficiency. They are also called range-extended electric vehicles for the obvious reason that the vehicles always have gasoline as a potential back-up that can extend the driving range. They are equipped with a larger and a powerful battery compared to HEVs, which can be recharged at the electricity grid.
PHEVs operate in two different modes based on the charge of the battery. It mostly uses electric motor to propel the engine which automatically reduces the fossil fuel consumption, and it will only switch to ICE if the battery level drops below the set limit.
Difference between Hybrid and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles
-
Basics of Hybrid and Plug-in Hybrid
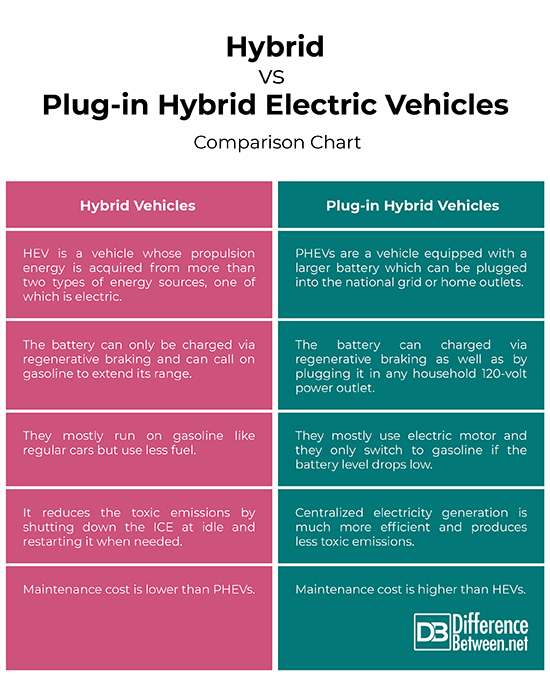
– Hybrid Electric Vehicles, or simply referred to as HEVs, are the most common types of electric vehicles that use a combination of two complimentary drive systems: electric motor with a battery and a petrol engine with a fuel tank. HEVs are the most practical alternative of the conventional vehicles because they are powered by both electricity and petrol. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles, or PHEVs, are hybrid vehicles with a larger and more powerful battery compared to HEVs that combine the benefits of a battery-powered electric vehicle and traditional hybrid vehicles.
-
Drive train
– The propulsion energy of HEVs come from more than two types of sources, one of which is an electric source. HEV drive trains are usually divided into three basic arrangements: series, parallel, and series-parallel hybrids. HEVs with a series drive train use two different energy sources that are combined in series; for the parallel HEV configuration, the vehicle uses both electric and mechanical traction sources; and for a series-parallel configuration, the vehicles combines the features of both series HEV as well as parallel HEV. PHEVs are based on the same three powertrain configurations, but unlike the hybrids, they can be plugged into the power grids.
-
Charging of Hybrid Vs. Plug-in Hybrid
– The internal combustion engine (ICE) is the main energy source that converts the original energy in gasoline to mechanical power and the mechanical energy is then converted into electric energy by a generator. The electric motor propels the vehicle using electricity generated by the generator or electricity stored in the battery. The batteries are charged using regenerative braking and gasoline in HEVs. PHEVs can be driven using electric energy stored in the onboard battery as well as the gasoline engine extends the driving range. The battery can charged via regenerative braking as well as by plugging it in any household 120-volt power outlet.
-
Emissions involves in Hybrid and Plug-in Hybrid
– In HEVs, battery is the power system to the internal combustion engine during vehicle propulsion which reduces the toxic emissions by shutting down the ICE at idle and restarting it when needed. With PHEVs, a significant amount of emissions can be reduced due to the reduced use of gasoline. Centralized electricity generation is much more efficient and produces less toxic emissions compared to HEVs which in turn helps mitigate the heavy pollution from the pollution-dense areas. This will have a long-term impact on the environment on the long run.
Hybrid vs. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Comparison Chart
Summary of Hybrid Vs. Plug-in Hybrid
Both HEVs and PHEVs are energy-efficient and environment-friendly hybrid electric vehicles that do not depend solely on an internal combustion engine as their only propulsion mechanism, instead they use bidirectional power flow. However, they have their fair share of differences in terms of efficiency, operating cost, maintenance cost, range, emissions, etc. Because PHEVs use electricity from the power grid, the reduced gasoline consumption results in better efficiency and less toxic emissions which contribute to a greener alternative.
Additionally, the electric motor increases system efficiency and reduces fuel consumption. Both the vehicles, however, operate in the same fashion, regardless of the architecture, but they are limited to short journeys.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Mi, Chris and M. Abul Masrur. Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Principles and Applications with Practical Perspectives. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2017. Print
[1]Pistoia, Gianfranco. Electric and Hybrid Vehicles. NYC: Elsevier, 2010. Print
[2]Shorten, Robert, et al. Electric and Plug-in Hybrid Vehicle Networks: Optimization and Control. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, 2017. Print
[3]Image credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/departmentofenergy/8284881948
[4]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/64/Plug-in_hybrid_electric_vehicle_%28PHEV%29_diagram.jpg/640px-Plug-in_hybrid_electric_vehicle_%28PHEV%29_diagram.jpg
