Difference Between Hydrogen Cars and Electric Cars
Electric vehicles are taking the world by storm, but there are some industry experts who believe hydrogen is the future of automotive industry. Car manufacturers are working on all sorts of new technology but there are two popular models which are creating a mass hype these days: one is the already popular electric car and the other is a car that uses hydrogen as fuel cells as an alternative fuel. Let’s see how the two compare.

What are Electric Cars?
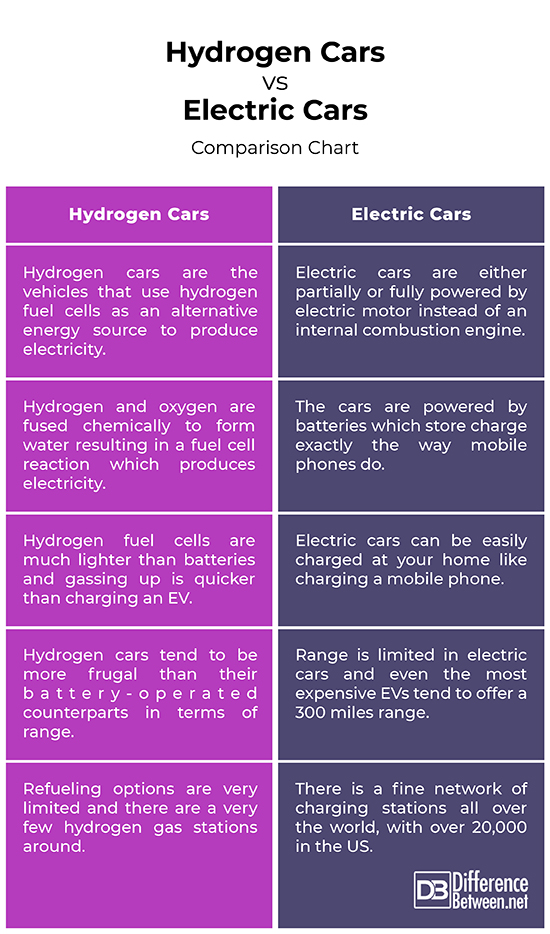
Electric cars, or more commonly known as EVs (Electric Vehicles), as the name suggest, are vehicles that are either partially or fully powered by electric motor instead of an internal combustion engine. The cars use a large battery pack to power the electric motor which, like a mobile, needs to be charged at a charging station or a wall outlet. Electric vehicles run on electricity, so they produce zero emissions from the tailpipe, which in turn benefits the environment in many ways. Electric cars are now starting to emerge as mainstream alternatives to internal combustion and petrol and diesel vehicles. They produce half the amount of carbon dioxide as a conventional car and they not only reduce noise and pollution, but also reduce the dependency of transport on oil. The trend in the performance of electric car sales can be traced back to the earliest days of the automotive industry. The resurgence of electric vehicles is a testament to recent advances in electric car technology.

What are Hydrogen Cars?
Hydrogen cars, or commonly goes by hydrogen fuel cell cars, are the vehicles that use hydrogen fuel cells as an alternative energy source to produce electricity. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are like all-electric vehicles that require electricity to power an electric motor, but instead of drawing electricity from battery, they draw power from a series of chemical reactions between hydrogen and oxygen. The possibility of using hydrogen as a general energy carrier has long been recognized. Hydrogen is often called the fuel of the future, providing a limitless supply of carbon-free, zero-emission energy. Hydrogen and fuel cells are touted as an excellent alternative to gasoline and combustion vehicles because they boast the performance of battery-powered electric cars, while providing greater range than any all-electric vehicle. Hydrogen is merely a replacement for gasoline and fuel cells are an alternative to internal combustion engines.
Difference between Hydrogen Cars and Electric Cars
Power
– Electric cars, often known as battery-powered electric vehicles, are vehicles that are either partially or fully powered by electric motor instead of an internal combustion engine. Electric cars are powered by batteries which store charge exactly the way phones do. They use a large battery pack to power the electric motor. Hydrogen cars, or commonly called hydrogen fuel cell cars, on the other hand, are kind of electric vehicles with a fuel tank meaning they run on motor powered by electricity. However, instead of a battery, they use hydrogen fuel cells to produce electricity which runs the motor.
Working
– Electric cars, as the name suggest, run on electricity stored in a large battery pack which powers an electric motor. The battery acts as a gas tank which supplies the motor with the required energy to move the vehicle. Hydrogen cars, on the other hand, use hydrogen gas to power an electric motor which produces electricity by combining hydrogen and oxygen. But, fuel cells do not burn the hydrogen. Instead, hydrogen and oxygen are fused chemically to form water resulting in a fuel cell reaction which produces electricity.
Efficiency
– Both hydrogen cars and electric cars are energy-efficient vehicles that are good for the environment because they do not emit carbon dioxide, which is a leading cause of global warming. However, they have their pros and cons. Hydrogen cars work just like gasoline but a lot more efficiently. Plus hydrogen is both zero-carbon and pollution free, and the hydrogen required to power their fuel cells could be produced using renewable energy technologies. But, depending on how the hydrogen gas is produced, hydrogen cars ultimately require more energy than electric cars. Electric vehicles produce zero emissions from the tailpipe, and they not only reduce noise and pollution, but also reduce the dependency of transport on oil.
Charging/Refueling
– Hydrogen fuel cells are much lighter than battery packs and you can top up your hydrogen car much faster than charging your electric car. Refueling a hydrogen car is similar to refueling an internal combustion engine, but the refueling options are very limited and there are a very few hydrogen gas stations because there aren’t many hydrogen cars around. So, the problem with hydrogen cars is that you cannot gas up anywhere and everywhere. Electric vehicles, on the other hand, can be easily charged at your home like charging a mobile phone, plus there’s a network of charging stations around which allows you to charge your EVs at a nominal cost.
Hydrogen Cars vs. Electric Cars: Comparison Chart
Summary of Hydrogen Cars vs. Electric Cars
Both hydrogen cars and electric cars are energy-efficient vehicles that are good for the environment because no gases are emitted from their exhausts, thereby reducing noise and pollution, and reducing our dependency on oil for transport. But electric cars appear to have an edge over their hydrogen counterparts, because of their availability, ease of charging, cost, and efficiency. However, hydrogen vehicles excel in the range category, which makes them a great alternative to electric vehicles. But the problem is that there aren’t many refueling stations around because there are not many hydrogen vehicles around. Given enough time and money, maybe we can see more hydrogen vehicles running around in the coming future.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Gerdes, Louise I. Hybrid and Electric Cars. Michigan, United States: Greenhaven Publishing, 2014. Print
[1]Gerdes, Louise I. Hybrid and Electric Cars. Michigan, United States: Greenhaven Publishing, 2014. Print
[2]Larminie, James and John Lowry. Electric Vehicle Technology Explained. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2012. Print
[3]Sørensen, Bent. Hydrogen and Fuel Cells: Emerging Technologies and Applications. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Academic Press, 2012. Print
[4]Grasman, Scott E. Hydrogen Energy and Vehicle Systems. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, 2016. Print
[5]Schutten, Jan Paul. Hello from 2030: The Science of the Future and You. New York, United States: Simon and Schuster, 2014. Print
[6]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/2627/3916687381_60632cae94_b.jpg
[7]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/6b/Electric_Car_recharging.jpg
