Differences Between Anxiety and Heart Attack
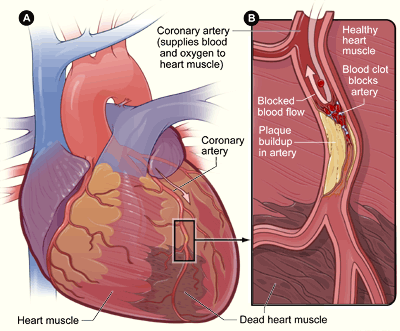
Diagram showing a
Difference between anxiety and heart attack
Introduction:
Patients suffering from heart related complaints may have a constant worry of having a heart attack. Anxiety causes the heart rate to elevate quickly and the force of each beat to increase. This abnormality of the heartbeat is termed as palpitation. A heart attack, or myocardial infarction, is a life threatening medical emergency in which the supply of blood to the heart is suddenly blocked, usually by a blood clot. Lack of blood to the heart can seriously damage the heart muscle. Anxiety on the other hand is the feeling of fear out of proportion to the situation.
Difference in Causes:
When one is suffering from an anxiety attack, the body releases adrenaline (a hormone produced during high stress situations) as the entire system prepares to go into fight or flight mode. This adrenaline rushes to the heart, causing the blood to pump out faster and the heart muscles to contract harder. This is the main cause of chest tightness and erratic heart palpitations during an anxiety attack.
On the other hand, a cardiac chest pain may be caused by any condition that affects the heart. The best example that can be cited here is that of chronic heart disease (CHD). CHD is a condition in which a waxy substance called plaque builds up within the coronary arteries (blood vessels of the heart) called atherosclerosis. Eventually, an area of plaque can break open inside and produce a blood clot. If the clot becomes large enough, it can partially or completely block blood flow through the artery resulting in lack of oxygen supply to the heart which leads to a heart attack. Heart attack, angina, and a coronary artery spasm are a few of the conditions that may lead to a chest pain.
Heart attack (myocardial infarction) warning signs in women.
Difference in Symptoms:
The symptoms of an anxiety attack and heart attack are closely related. Anxiety leads to sweating, trembling, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, chest pain, breathlessness, feeling of impending doom or death, dizziness, etc. The other symptoms which may occur are tingling in legs, headache and chest pain.
The chest pain felt during an anxiety attack tends to be more localized, usually away from the centre of the chest and lasts less than a 3-5 minutes. Cardiac complaint-related chest pain is felt at the centre of the chest, and tends to radiate over the left shoulder or arm or into the upper back or jaw. This radiating kind of pain is one of the characteristics of a cardiac chest pain and is not seen in anxiety related chest pains.
Anxiety related chest discomfort tends to be milder. On the other hand, cardiac chest pain tends to be duller, and in some ways it feels like the heart is being crushed or one feels choked. Some patients describe the pain as a heavy weight on the heart, a crushing sensation. In an anxiety attack, you can feel like your heart is being squeezed, but with cardiac chest pain that squeezing tends to be far more pronounced and usually lasts longer than 10-30 minutes and gets immediately relieved with rest and oral nitrates.
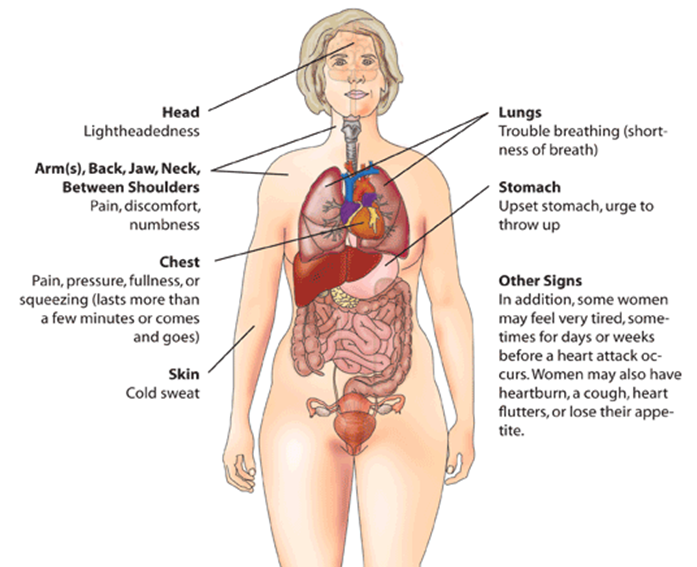
The symptoms of a heart attack are chest discomfort, pressure, heaviness, or pain in the chest, arm, or below the breastbone. There may also be a feeling of fullness or indigestion associated with an oncoming attack. Sweating, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, extreme weakness, anxiety and shortness of breath are the other associated symptoms of a heart attack.
Treatment for heart attack is immediate rest and hospitalisation to open up the blocked cardiac supply. Treatment of anxiety attacks is by going away from the situation causing anxiety, breathing into a brown bag and tranquilizers.
Summary:
Anxiety is a natural bodily response that helps us at a very basic level to cope with situations whereas a heart attack occurs in people with heart-related disorders. Presenting symptoms are similar although in a heart-attack the intensity of chest pain is far worse.
- Difference between near sightedness and far sightedness - January 21, 2015
- Difference between Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis - January 20, 2015
- Difference between Prilosec and Nexium - January 19, 2015

What about all of the medical websites that list all of the different types of heart attacks, some of which do not follow the “classic heart attack” symptoms? The heart attacks that happen to otherwise healthy people, with no history of heart disease? In my humble opinion, before writing an article like this, you should really do your research as what you posted here is very misleading.