Difference Between Botany and Horticulture
What is Botany and Horticulture?
Both the terms deal with plants. The science-based knowledge in both the scientific fields are exchangeable. For instance, botanical science experts and specialists can apply the scientific knowledge in horticulture field, and the vice-versa. Both botanist and the horticulturist can work in the same department and vice-versa.
However, there are differences as well in both the scientific fields. Horticulture involves garden management and cultivation. Botanical science is a broader field. It involves focus on plants as a whole and traditionally includes classification of plant species.

What is Botany?
Botany is defined as the scientific study of plants, including their physiology (the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system), structure, genetics (branch of biology concerned with the study of variation in genes, genes, and heredity) ecology (science that studies the biota (living things), the environment, and their interactions), distribution, classification, and economic importance.

What is Horticulture?
Horticulture is defined as the art and science of sustainable production, garden cultivation, intensively cultivated food and ornamental plants and management. It also includes plant conservation, landscape restoration (planned process of restoring ecological integrity), soil management, landscape and garden design, and arboriculture (the cultivation and nurturing of trees, shrubs, vines, and woody plants).
Difference between Botany and Horticulture
Definition
Botany
It is a study of science of plants. The study emphasizes how plants function on a cellular/physiology level.
Since it is a study of plants, it also includes the study of classification, distribution, ecology, genetics, structure, and physiology.
Horticulture
The study is a combination of science and art with the purpose of cultivating and managing gardens and plants.
Horticulture involves growing the plants for aesthetic purposes. It is also involved in the maintenance and landscaping of parks, national and regional gardens and fields, golf courses, and other public gardens.
Branches
Botany
- Agricultural Science – study of plants that are of economic importance
- Algology – or Phycology is the study of algae
- Arboriculture – study of propagation of trees
- Bacteriology – study of bacteria
- Agrostology – study of grasses
- Bryology – study of mosses, liverworts and hornworts
- Agronomy – production of plant crops and management of soil
- Dendrology – study of woody plants such as shrubs and trees
- Economic Botany – study of economic uses of plants and plant products
- Ethnobotany – study of plants and their relationship with humans
- Horticulture – study of Cultivation of plants
- Lichenology – study of lichens
- Plant Biotechnology – application of plants and plant products for human welfare
- Palynology – study of pollen grains and spores
- Plant Cell Biology – study of plant cells and related process
- Mycology – study of fungi
- Orchidology – study of orchids
- Plant Genetics – study of genes and genetic inheritance in plants
- Phenology – study of timing of root and shoot germination, flowering and fruiting
- Plant Anatomy – the study of structural properties of plants
- Paleobotany – study of plant fossils
- Plant Biochemistry – study of chemical processes and molecules involved in plants
- Plant Pathology – study of diseases in plants
- Plant Physiology – study of plant processes and functions
- Pomology – study of fruits and nuts
- Plant Tissue Culture – also termed as micropropagation, is the study of rapid propagation in plants
- Plant Reproduction – study of reproduction in plants
- Pteridology – study of pteridophytes and ferns
- Plant Taxonomy – classification and naming of plants
- Plant Ecology – study of environment and its relationship with plants
- Rhodology – study of roses
Horticulture
- Pomology – cultivation of fruit crops
- Floriculture – cultivation of flower crops
- Plantation Crops – cultivation of crops like coconut, arecanut, rubber, coffee
- Olericulture – cultivation of vegetables
- Post-Harvest Technology – post-harvest handling, packaging, storage, grading, processing, marketing, value addition, marketing etc. of horticulture crops
- Spices Crops – cultivation of crops like, black pepper, cardamom, nutmeg
- Plant Propagation – propagation of plants
- Medicinal and Aromatic Crops – cultivation of medicinal and aromatic crops
Job Responsibilities
Botany
Job responsibilities of a plant scientist include:
- Review and investigate essays and other documents containing analysis of plants and soil and rainfall trends
- Collection and testing samples of plants and documenting results and observations
- Work towards conserving and restoring botanical establishments, such as rainforests
- Follow and document agricultural crop productivity
- Conducting field work and tracking and locating endangered or new species of plants
Horticulture
Job responsibilities of a horticulturist include:
- Oversee the growth, harvest, packaging, selling and distribution of ornamental plants and crops
- Plant trees and lay grass seed
- Offer technical information and knowledge to flower, fruit, veggie growers as well as farmers
- Create flower arrangements or build large, outdoor arrangements of bushes and shrubs
- Weed and trim flowers, shrubs, and lawns
- Mow and water lawns for various residential establishments and businesses clients
Application
Botany
Contributes to development of new medicines and treatments for major diseases. Helps farmers use modern and optimum plant growing and cultivation techniques to boost and enhance efficiency and effectiveness when growing crops.
Horticulture
Horticulture crops are more suitable for small and marginal farmers. It beautifies the surroundings. Horticulture enriches diets.
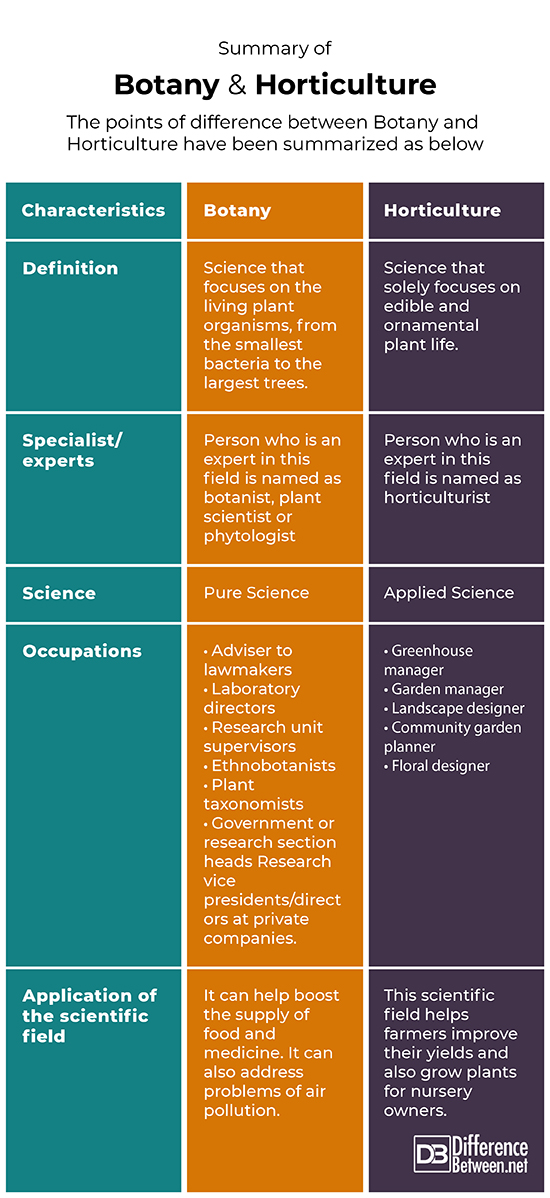
Summary of Botany and Horticulture
The points of difference between Botany and Horticulture have been summarized as below:
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Arteca, R. N. (2014). Introduction to horticultural science. Nelson Education.
[1]Arteca, R. N. (2014). Introduction to horticultural science. Nelson Education.
[2]Holland, D., Hatib, K., & Bar-Ya’akov, I. (2009). Pomegranate: botany, horticulture, breeding. Horticultural reviews, 35(2), 127-191.
[3]Morton, A. G. (1981). History of Botanical Science. An account of the development of botany from ancient times to the present day. Academic Press.
[4]Uno, G. E. (2009). Botanical literacy: What and how should students learn about plants? American journal of botany, 96(10), 1753-1759.
[5]Image credit: https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2020/03/27/11/07/horticulture-4973295_960_720.jpg
[6]Image credit: https://www.pexels.com/photo/agriculture-background-botany-concept-1214392/
