Difference Between Orthopedic Surgery and Neurosurgery
What are Orthopedic Surgery and Neurosurgery?
Neurosurgeons are medical specialists who are well trained to treat patients suffering from spinal cord or brain conditions, while people who suffer from complex spine issues usually would consult an orthopedic surgeon.
Both specialists carry out surgeries on spine, both specialize to offer cutting-edge, negligibly intrusive techniques and both can specialize in the spine. However, both specialties are very different and offer different surgical results.
What are the Similarities between Orthopedic Surgery and Neurosurgery?
Both surgeons are given specialized training in all aspects of spine health to help people with spinal and neurological conditions.
Orthopedic Surgery
Orthopedic surgeons address issues and disorders associated with the musculoskeletal system comprising of tendons, nerves, bones, joints, ligaments, and skin. Some injuries and disorders addressed by orthopedic surgeons include the torn ligaments (a membranous fold that supports an organ), damaged and broken bones, sprains, tendon injuries, bone tumors (bone neoplasm) and arthritis. Orthopedic surgeons treat patients with both surgical intervention (procedures that involve surgery) and noninvasive care.
Neurosurgery
Neurosurgeons address conditions associated with the central nervous system (brain) and the spinal cord. Their primary job is to eliminate chances and risks of tumors, congenital anomalies (an often-inherited medical disorder that happens at or before birth), infections and other traumatic injuries.
Difference between Orthopedic surgery and Neurosurgery
Description
Orthopedic surgery
Surgeries associated with issues of musculoskeletal system
Neurosurgery
Surgeries associated with issues of brain and spinal cord
Specialization
Orthopedic surgery
An orthopedic surgeon or specialist is well trained to identify disorders and issues associated with your musculoskeletal system. His main job is to stabilize and enhance the functioning of your bones, joints, spine, muscles, nerves, ligaments, and tendons and these are all part of the musculoskeletal system. To be precise, the primary responsibility of an orthopedist is to figure out the source of your musculoskeletal pain and to erase it.
For e.g., orthopedists or specialists who have done specialization in spine surgery address disorders of spine like;
- Spinal deformities (an abnormal alignment or curve of the bony vertebral column), such as adult and pediatric scoliosis (caused by age-related wear and tear), kyphosis, lordosis, or flatback syndrome
- Degenerative or age-related spine conditions, such as degenerative disc disease, bulging or herniated discs, spinal stenosis, osteoporosis, spondylolisthesis, etc.
- Osteoarthritis (Arthritic spine issue), facet joint disease (an arthritis-like condition of the spine), and ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew’s disease)
- Radiculopathy (A disorder of the root of a nerve, or a pinched nerve condition – cervical, thoracic or lumbar, such as sciatica (sciatic neuritis) or disease process marked by nerve compression (cervical radiculopathy)
- Sports spine injuries, – traumatic strains, spinal cord injuries or sprains
- Osteomyelitis (infection of bone) and Vertebral column tumors (extradural tumors that occur in the exterior of the spinal cord itself). These are spinal infections.
Neurosurgery
A neurosurgeon is a medical specialist that is specialized to emphasize primarily on the central nervous system and its communication/imparting with the rest of the body. A neurosurgeon is well trained and with experience and more and more practice is able to address multiple central nervous system (brain) and spine disorders, including:
- Brain tumors (a malign or benign mass of abnormal growth of cells in the brain)
- Intradural tumors (i.e., tumors that begin within the Dural sheath or covering of the spinal cord
- Birth defects, such as tethered spinal cord syndrome or spina bifida
- Strokes, aneurysms (ballooning and weakened area in an artery), and clinical syndrome that results because of disrupted blood supply (cerebrovascular events)
- Epilepsy (A condition in which activity of nerve cell in the central nervous system is disturbed, resulting in seizures)
- Parkinson’s disease (brain disorder that impacts movement including shakiness, tremors, difficulty walking etc.) dystonia (a very complex and variable movement disorder), or essential tremor (Movement disorders)
- Neurological disorders like Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) or Multiple Sclerosis
- Chronic pain conditions that impact the brain or the peripheral nervous systems
Differences in Recovery Strategies
Orthopedic surgery
Surgical procedures to treat disorders of the musculoskeletal system
- Shoulder and rotator cuff surgery
- ACL surgery
- Arthroscopic surgery
Neurosurgery
Surgical procedures to treat disorders of the nervous system
- Deep brain stimulation (DBS)
- Endovascular procedures, Carotid endarterectomy (to treat carotid artery disease), Coil embolization (a catheter-based method that enables precise occlusion of blood flow that is not normal in a blood vessel)
- Peripheral nerve surgery, Carpal tunnel release, Ulnar nerve release
- Spine surgery, Discectomy, Laminectomy.
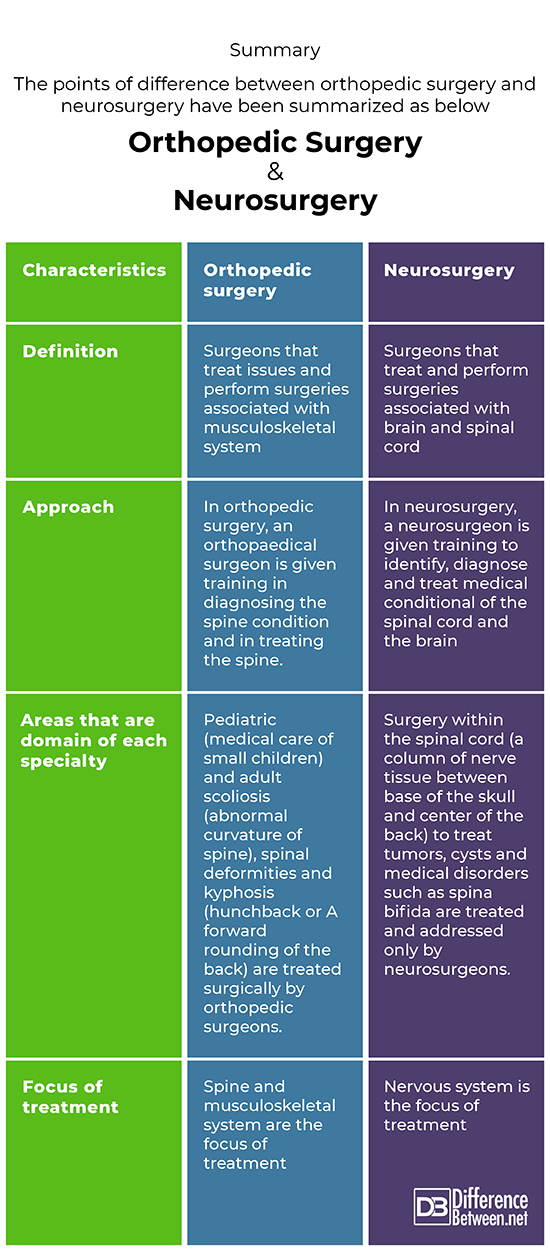
Summary
The points of difference between orthopedic surgery and neurosurgery have been summarized as below:
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Cha, C. W. (2012). U.S. Patent No. 8,221,424. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.
[1]Esene, I. N., El-Shehaby, A. M., & Baeesa, S. S. (2016). Essentials of research methods in neurosurgery and allied sciences for research, appraisal and application of scientific information to patient care (Part I). Neurosciences, 21(2), 97.
[2]Lu, C., Buckley, J. M., Colnot, C., Marcucio, R., & Miclau, T. (2009). Basic research in orthopedic surgery: current trends and future directions. Indian journal of orthopaedics, 43(4), 318.
[3]Malige, A., Yuh, R., Yellapu, V., Lands, V., Woods, B., & Sokunbi, G. (2020). Review of physician referrals to orthopedic spine versus neurosurgery. Clinics in orthopedic surgery, 12(1), 55.
[4]Image credit: https://www.picpedia.org/medical/images/neurosurgery-services.jpg
[5]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:After_orthopedic_surgery.JPG
