Difference Between Canonical and Noncanonical

Canonical (conforming to a general rule or acceptable procedure) often refers to established pathways with typical or standard characteristics in biological investigation. A non-canonical (not sanctioned by a canon) feature is one that scientists discover in an established pathway but which does not conform (keep to) to the canonical model.
Similarity
Both canonical and noncanonical may be semi-redundant (superfluous), which means that there could be process(es) or systems where these pathways converge.
Canonical
The intracellular buildup of Beta-catenin and the subsequent translocation (occurs when a chromosome breaks and the (typically two) fragmented pieces re-attach to different chromosomes) of the protein to the nucleus (a specialized structure occurring in most cells (except bacteria and blue-green algae), where it controls the expression of target genes (the process of altering a specific sequence or gene at its location in a genome), constitute the canonical route.
Inflammatory and immune response genes are expressed when the canonical route is activated. Because prolonged NF-B activation can result in abnormal gene expression and because improper control of NF-B activation has been linked to diseases including cancer and chronic inflammation, these signals must be brief and effectively managed. There are many systems that have developed to allow for post-induction attenuation or termination of signaling, thus it is not surprising that this is the case.
Noncanonical
The term “non-canonical pathways” refers to biogenesis (the process wherein life arises from similar life forms) pathways that do not follow the canonical paradigm (idealized or generalized features, for example, in biochemical pathways) or that only partially conform to it. Non-canonical (not sanctioned by a canon) routes are occasionally other, less well-known pathways.
A NEMO-independent IKK1 kinase complex 59 is responsible for activating the non-canonical NF-B pathway (nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells). According to recent studies, this pathway’s activation depends on the controlled assembly of the upstream signaling complex that includes the cellular inhibitors of apoptosis (cIAP1 and cIAP2), TRAF2 (TNF receptor-associated factor 2) and TRAF3 (TNF Receptor Associated Factor 3), and NIK. The activation of cIAPs and K63-linked ubiquitination by TRAF2 happen as a result of the TRAF2 (TNF receptor-associated factor 2) -dependent recruitment of cIAP1 (also named BIRC2) and cIAP2 (the cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 2) upon receptor interaction. TRAF3 functions as an adaptor molecule that enables the formation of a complex including NIK, TRAF2 (TNF receptor-associated factor 2), and activated cIAPs, which results in the modification of TRAF3 by cIAPs through K48-linked ubiquitination.
Difference between canonical and noncanonical
Definition
Canonical
The canonical pathway consists of the intracellular (located or occurring within a cell or cells) accumulation of Beta -catenin and the subsequent translocation of the protein (phenomenon that results in unusual rearrangement of the proteins) to the nucleus, where it regulates (manages) the expression of target genes.
The adverb canonical is used to describe something as being “according to the canon” in a variety of settings. The canon is the acknowledged standard, law, or fundamental source for the body of knowledge or body of literature in that area.
Noncanonical
The non-canonical pathway (an important arm of NF-κB (a key transcription factor of M1 macrophages) signaling that predominantly targets activation of the p52/RelB NF-κB complex) is defined by its Beta-catenin-independent actions ranging from intracellular (located or occurring within a cell or cells) signaling and expression of target genes. These are alternative fewer known pathways.
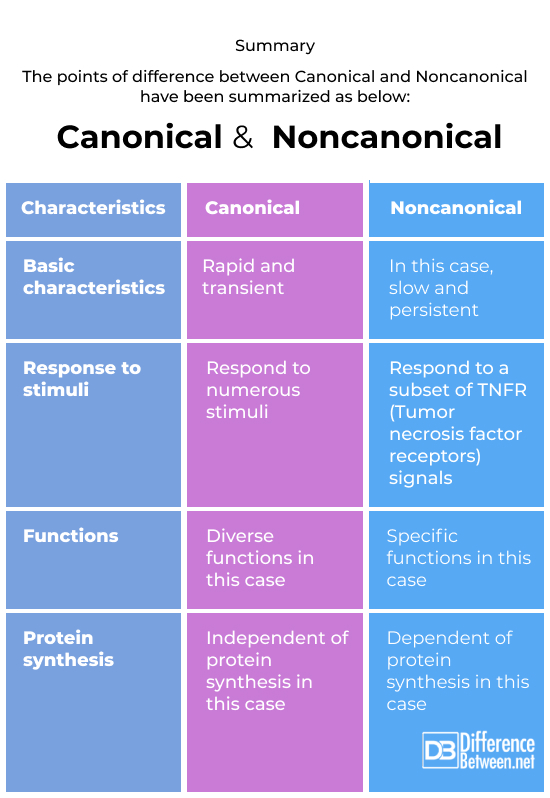
Summary
The points of difference between Canonical and Noncanonical have been summarized as below:
FAQ:
What is a non-canonical mutation?
The term “non-canonical mutations” (deviate from the canonical paradigm) involves all mutations other than R132H IDH1 (reduces proliferation, cell survival) alterations.
What is non-canonical literature?
Non-canonical literature is very influential. Non-canonical literature is different in variability in lower case text properties.
What is canonical signaling?
Canonical describes the pathway elements that result in stabilizing (to make stable, steadfast) beta-catenin (also known as Catenin beta-1) in response to certain Wnt ligands.
What are the non-canonical Wnt target genes?
Non-canonical Wnt target genes are dependent on RoR2 (Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Like Orphan Receptor 2), Dvl2 (Dishevelled Segment Polarity Protein 2), ATF2 (Activating transcription factor-2) and ATF4.
What is canonical vs normal?
In different subfields (more specialized area of study or occupation within a larger one), “canonical” and “normal” forms are distinguished differently. A normal form just describes a product’s form without the condition of uniqueness (the quality of being particularly remarkable), whereas a canonical (conforming to a general rule or acceptable procedure) form in most fields specifies a unique (one of its own kind) representation for each object.
What is a noncanonical nucleotide?
Numerous of the more than one-fifty noncanonical nucleotides that have been found in the tRNA (Transfer RNA is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA) molecules of various animals are among the noncanonical (not sanctioned by a canon) nucleotides, which are modified versions of the canonical nucleotides.
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Bahlmann, J., Rodriguez‐Fornells, A., Rotte, M., & Münte, T. F. (2007). An fMRI study of canonical and noncanonical word order in German. Human brain mapping, 28(10), 940-949.
[1]Connolly Jr, H. C., & Jones, R. H. (2016). Chondrules: The canonical and noncanonical views. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 121(10), 1885-1899.
[2]Di Luca, S., & Pesenti, M. (2010). Absence of low-level visual difference between canonical and noncanonical finger-numeral configurations. Experimental Psychology.
[3]Mohseni, M., Redies, C., & Gast, V. (2022). Approximate entropy in canonical and non-canonical fiction. Entropy, 24(2), 278.
[4]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MADQ5snsZXc-stethoscope-on-a-medical-record/
[5]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAEbrGf_1bU/
