Difference Between Thermal Printer and Inkjet Printer
Individuals and businesses around the world rely on printers for their day-to-day uses to print all sorts of stuffs, including receipts, documents, banners, signs, and more. We take a look at two of the most commonly used printers – Thermal printers and Inkjet printers – and try to understand the differences between the two.
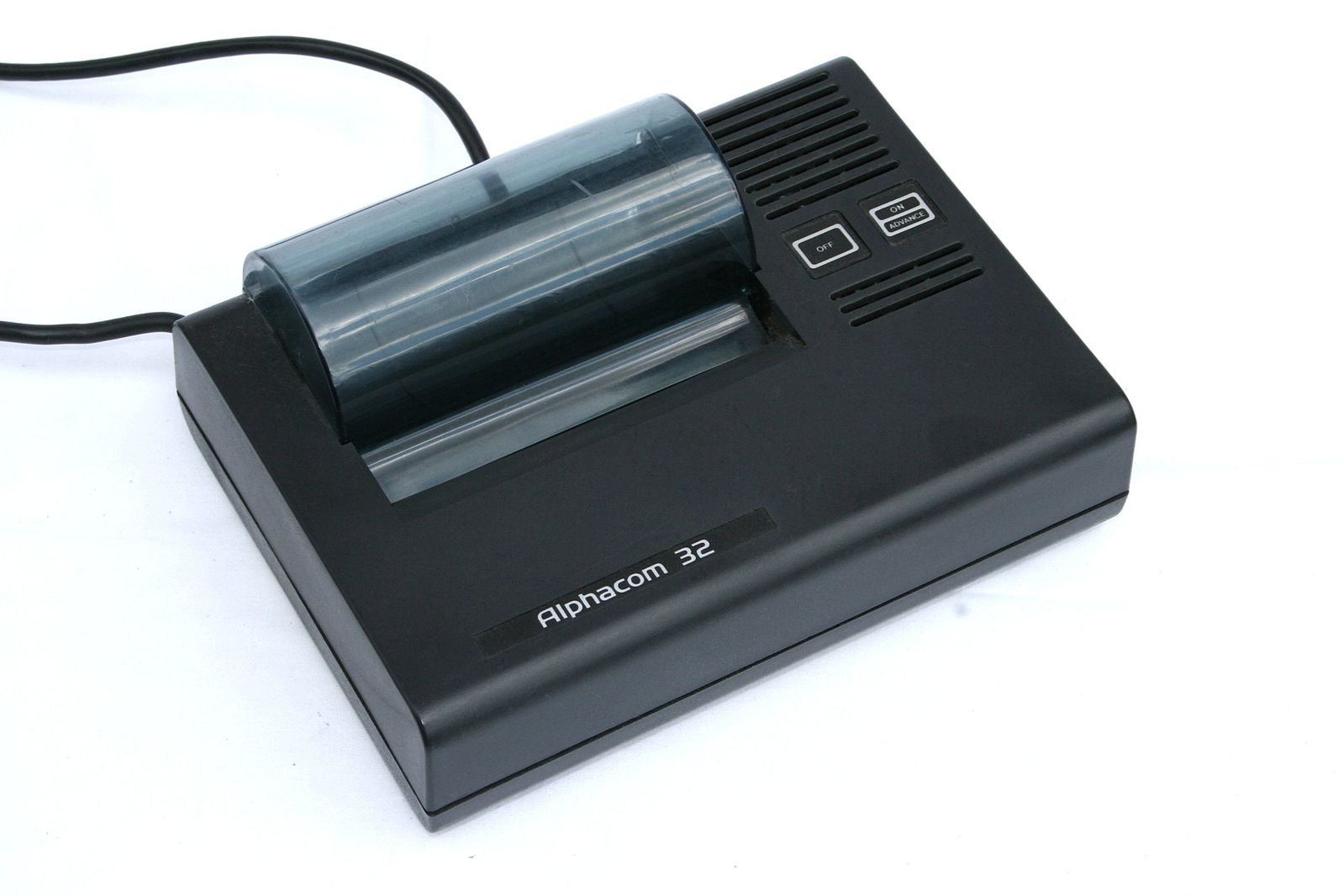

What is Thermal Printer?
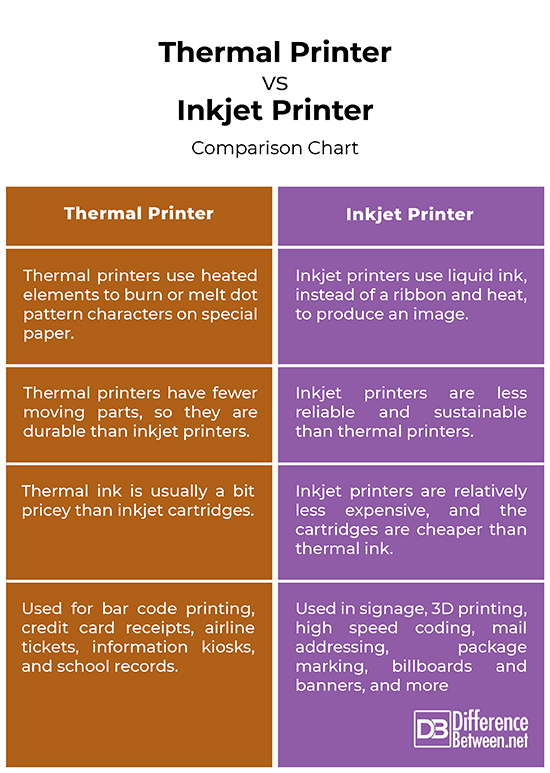
Thermal printers are low-cost, portable printers that are commonly used to print receipts and shipping labels. Thermal printers, as the name suggest, use a heated print head to produce the image on paper. They use heated elements to burn or melt dot pattern characters on special paper. The thermal print head is the core of the thermal printing system, which consists of a fixed array of microscopic heating elements. When electricity is applied to the resistor elements, heat is generated in the area under the elements. Two types of thermal printers are mainly used: direct transfer thermal printers and thermal wax transfer printers. Today, thermal printers are widely used for bar code printing, credit card receipts, airline tickets, and school records. These printers do not rely on ink to print, which keeps the cost lower.
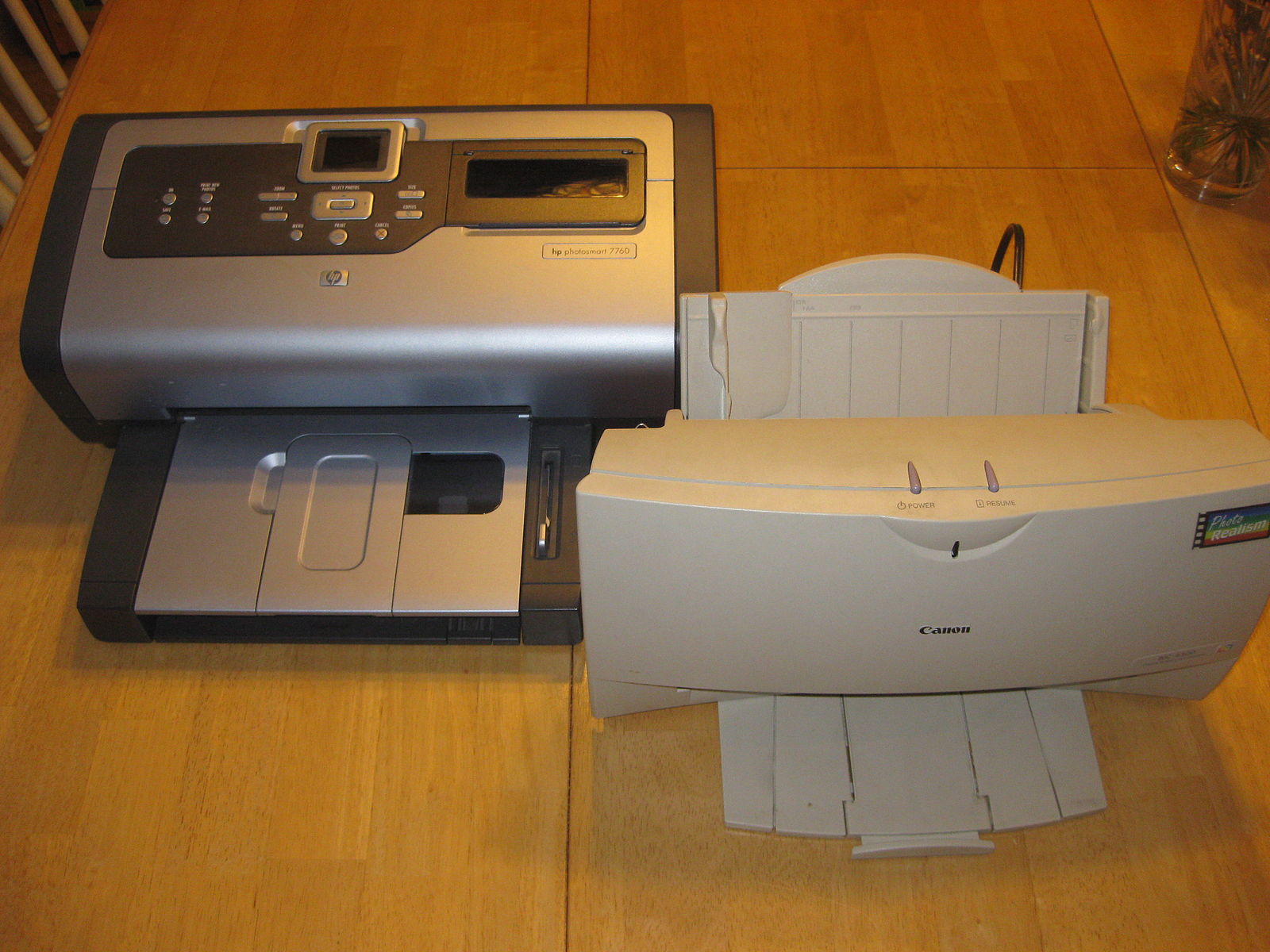

What is Inkjet Printer?
Inkjet printers are the most popular choice of printer for home printing needs. They are the most abundant techniques of digital printing, widely used in offices and in industrial applications such as wide format printing. As the name suggests, the printing is done with the help of inkjet technology – an image is created by precisely spraying thousands of tiny ink droplets onto a substrate, such as paper, pixel by pixel. The printing process is quite complicated, and requires delicate tailoring of the chemical and physicochemical properties of the ink. By carefully managing the size, placement, and color of the dots, the printer produces a print that appears as a continuous tone print when viewed. They are the most affordable, quick, and convenient method of printing digital files. They are widely used for high speed coding, mail addressing, package marking, billboards and banners, and wide format graphics for signs.
Difference between Thermal and Inkjet Printer
Printing Process
– Thermal printers use heated elements to burn or melt dot pattern characters on special paper. It’s a cost-effective industrial printing technique that uses dry, wax based pigment into the substrate, such as paper using heat. The print head does not move across the page; instead it scans across the paper, printing a row of characters. Inkjet printers, on the other hand, use liquid ink, instead of a ribbon and heat, to produce an image – the printer sprays thousands of tiny ink droplets onto a substrate, such as paper, pixel by pixel to create an image.
Image Quality
– Inkjet printers are among the most abundant methods of digital printing that can produce high-quality images at a lower initial cost. The two main determinants of print quality are resolution, the substrate used in printing, and the number of levels that can be printer per dot. Any moisture or humidity can damage the prints. Thermal printers produce higher quality prints with a glossy, protective finish and better color saturation. Because thermal printers have fewer moving parts, they are durable.
Equipment Cost
– Although, thermal printers do not require ink, the specialty materials used in the printing process can be considerably expensive. However, in bar code applications, no other printing technology can beat the image sharpness of thermal printing anywhere near the price. Thermal ink is usually a bit pricey than inkjet cartridges. Inkjet printers are relatively less expensive and the cartridges are cheaper than thermal ink. In addition, the cartridges can be refilled and reused, saving money.
Applications
– Thermal printers are widely used for bar code printing, credit card receipts, airline tickets, and school records. Commercial applications of thermal printers include information kiosks, filling stations, POS systems, shipping labels, etc. Inkjet printers are widely used in offices and in industrial applications for wide format printing. They are mainly used for a variety of industrial applications such as signage, 3D printing, high speed coding, mail addressing, package marking, billboards and banners, and more.
Thermal Printer vs. Inkjet Printer: Comparison Chart
Summary
While both thermal printing and inkjet printing are widely used printing methods, they are very distinct processes. Thermal printers use heated elements to burn or melt dot pattern characters into special thermal paper. Thermal printing is widely used for battery powered handheld printing devices, bar code printing, and credit card receipts printing. Thermal printers are more sustainable and reliable than their inkjet counterparts because of the fact that they have fewer moving parts. Inkjet printers produce characters by squirting a precisely controlled stream of ink dots onto the paper. Although, inkjet printers are relatively less expensive to procure and maintain, they are not very reliable.
Is a thermal printer better than inkjet?
Thermal printers have fewer moving parts, which makes them easy to maintain, more sustainable and durable for long term use. However, thermal printers are also more expensive than inkjet printers.
Can I use thermal paper for inkjet printer?
Thermal papers are specially designed for use in thermal printers. So, thermal papers cannot be used for inkjet printing. Also, you cannot use normal papers in thermal printers.
What is the difference between a thermal printer and a regular printer?
Regular printers are mainly used to print on letter-size paper using dye-based ink or laser printer toner. Laser printers and inkjet printers are probably the most used printers for home and office applications. Unlike regular printers, thermal printers do not use liquid ink to produce images.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Brooks, Charles J. A+: Training Guide. Seattle, United States: Que Publishing, 2003. Print
[1]Diamond, Arthur S. Handbook of Imaging Materials, Second Edition. Florida, United States: CRC Press, 2001. Print
[2]Nickelson, Jim. Fine Art Inkjet Printing: The Craft and Art of the Fine Digital Print. California, United States: Rocky Nook, Inc., 2008. Print
[3]Magdassi, Shlomo. The Chemistry Of Inkjet Inks. Singapore: World Scientific, 2009. Print
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Inkjet_printers.jpg
[5]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Alphacom_32_thermal_printer_(7101899885).jpg
