Difference Between Dizziness and Tinnitus
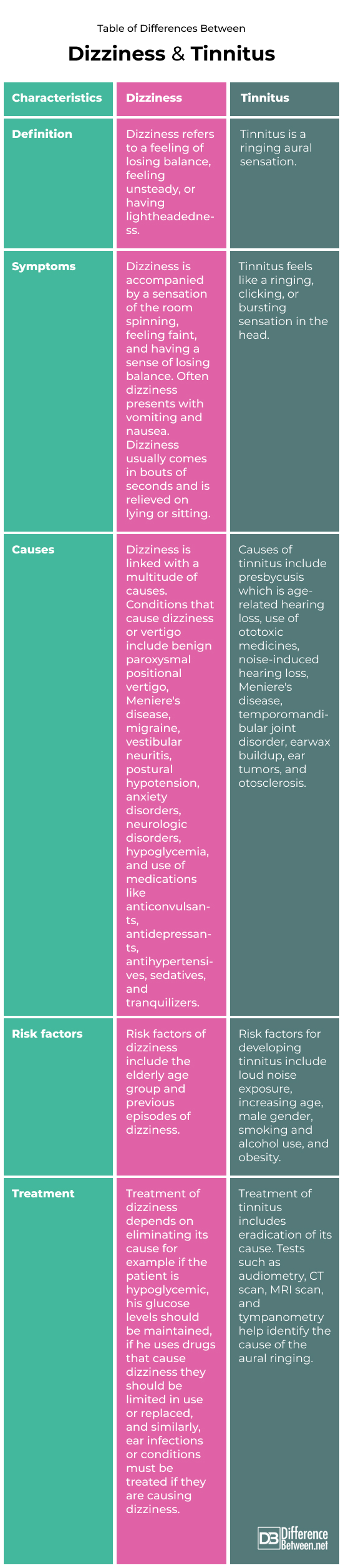
Dizziness refers to a feeling of losing balance, feeling unsteady, or having lightheadedness. Vertigo is also used interchangeably with dizziness. It is a sensation of the room spinning around you. Tinnitus is a ringing aural sensation.

What is dizziness?
Definition:
Dizziness refers to a feeling of losing balance, feeling unsteady, or having lightheadedness.
Symptoms:
Dizziness is accompanied by a sensation of the room spinning, feeling faint, and having a sense of losing balance. Often dizziness presents with vomiting and nausea. Dizziness usually comes in bouts of seconds and is relieved on lying or sitting.
Causes:
Dizziness is linked with a multitude of causes. Conditions that cause dizziness or vertigo include benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, Meniere’s disease, migraine, vestibular neuritis, postural hypotension, anxiety disorders, neurologic disorders, hypoglycemia, and use of medications like anticonvulsants, antidepressants, antihypertensives, sedatives, and tranquilizers.
Risk factors:
Risk factors of dizziness include the elderly age group and previous episodes of dizziness.
Treatment:
Treatment of dizziness depends on eliminating its cause for example if the patient is hypoglycemic, his glucose levels should be maintained, if he uses drugs that cause dizziness they should be limited in use or replaced, and similarly, ear infections or conditions must be treated if they are causing dizziness.

What is Tinnitus?
Definition:
Tinnitus is a ringing aural sensation.
Symptoms:
Tinnitus feels like a ringing, clicking, or bursting sensation in the head. It is a ringing sound in the ear that no one else can hear except the affected individual.
Causes:
Causes of tinnitus include presbycusis which is age-related hearing loss, use of ototoxic medicines, noise-induced hearing loss, Meniere’s disease, temporomandibular joint disorder, earwax buildup, ear tumors, and otosclerosis.
Risk factors:
Risk factors for developing tinnitus include loud noise exposure, increasing age, male gender, smoking and alcohol use, and obesity.
Treatment:
Treatment of tinnitus includes eradication of its cause. Tests such as audiometry, CT scan, MRI scan, and tympanometry help identify the cause of the aural ringing.
Difference between Dizziness and Tinnitus
Definition:
Dizziness refers to a feeling of losing balance, feeling unsteady, or having lightheadedness. Tinnitus is a ringing aural sensation.
Symptoms:
Dizziness is accompanied by a sensation of the room spinning, feeling faint, and having a sense of losing balance. Often dizziness presents with vomiting and nausea. Dizziness usually comes in bouts of seconds and is relieved on lying or sitting. Tinnitus feels like a ringing, clicking, or bursting sensation in the head.
Causes:
Dizziness is linked with a multitude of causes. Conditions that cause dizziness or vertigo include benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, Meniere’s disease, migraine, vestibular neuritis, postural hypotension, anxiety disorders, neurologic disorders, hypoglycemia, and use of medications like anticonvulsants, antidepressants, antihypertensives, sedatives, and tranquilizers.
Causes of tinnitus include presbycusis which is age-related hearing loss, use of ototoxic medicines, noise-induced hearing loss, Meniere’s disease, temporomandibular joint disorder, earwax buildup, ear tumors, and otosclerosis.
Risk factors:
Risk factors of dizziness include the elderly age group and previous episodes of dizziness. Risk factors for developing tinnitus include loud noise exposure, increasing age, male gender, smoking and alcohol use, and obesity.
Treatment:
Treatment of dizziness depends on eliminating its cause for example if the patient is hypoglycemic, his glucose levels should be maintained, if he uses drugs that cause dizziness they should be limited in use or replaced, and similarly, ear infections or conditions must be treated if they are causing dizziness. Treatment of tinnitus includes eradication of its cause. Tests such as audiometry, CT scan, MRI scan, and tympanometry help identify the cause of the aural ringing.
Table of differences between dizziness and tinnitus
FAQs
What is the difference between tinnitus and vertigo?
Tinnitus is aural ringing whereas vertigo is feeling lightheaded or a sensation of the room spinning.
How do I know if my dizziness is ear related?
If dizziness is accompanied by vertigo, tinnitus, and loss of balance then it is likely due to an ear problem.
Can tinnitus make you dizzy and off balance?
Yes, often tinnitus is accompanied by vertigo.
How long does dizziness last with tinnitus?
For minutes to hours.
How do you know if dizziness is serious?
Dizziness is serious if it comes with a new numbness, especially in the limbs or face, slurry speech, visual problems, and confusion.
What is the treatment for dizziness and tinnitus?
Treatment of dizziness and tinnitus is the eradication of its cause. Tests such as audiometry, CT scan, MRI scan, and tympanometry help identify the cause of the aural ringing.
Why are my ears ringing and my head feels weird?
Likely due to a vestibular disorder.
What are two signs of Meniere’s disease?
Deafness, vertigo, and tinnitus.
What inner ear problems cause dizziness?
Vestibular neuritis, acoustic neuroma and benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.
- Differences Between Reptiles and Amphibians - May 17, 2024
- Difference Between Ophthalmology and Optometry - May 15, 2024
- Difference Between Fear and Anxiety - April 2, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Hoffman, Richard M., Douglas Einstadter, and Kurt Kroenke. "Evaluating dizziness." The American journal of medicine 107.5 (1999): 468-478.
[1]Kroenke, Kurt, Richard M. Hoffman, and Douglas Einstadter. "How common are various causes of dizziness? A critical review." Southern medical journal 93.2 (2000): 160-7.
[2]Baguley, David, Don McFerran, and Deborah Hall. "Tinnitus." The Lancet 382.9904 (2013): 1600-1607.
