Difference Between Aneurysm and False Aneurysm
An aneurysm is formed when a bulge or swelling is formed in the wall of a blood vessel due to weakness of the wall. A false aneurysm is when blood pools in the surrounding tissues of the injured wall of blood vessels.

What is an Aneurysm?
Definition
A slight bulge in the wall of an artery is called an Aneurysm. They are formed because of soft areas present in the walls of arteries. They can result in uncontrolled bleeding and prove fatal if left untreated for an extended period of time.
Types of Aneurysms
There are different types of aneurysms depending on where they are located. They can be located in the brain, legs, heart, and abdomen.
- Cerebral Aneurysm
- Thoracic aortic aneurysm
- Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
- Popliteal aneurysm
- Mesenteric Artery Aneurysm
- Splenic Artery Aneurysm
Symptoms
Aneurysms mostly act as silent killers. People don’t feel any symptoms when they are unruptured. The ruptured aneurysms can show the following symptoms:
- Tachycardia
- Lightheadedness
- Severe headache following the loss of consciousness
- Sharp pain in the back, abdomen, chest, or head.
A ruptured Aneurysm is a medical emergency; you must call 911 when there is a possibility of internal bleeding as it can be fatal.
Moreover, other symptoms depend upon the location of the aneurysm. An abdominal aneurysm can present with nausea, vomiting, pulsating mass can be felt in the abdomen, and sharp pain in the abdominal region.
Passing out, confusion, rapid heartbeat and changes in vision can be signs of Brain Aneurysms.
Complications
An aneurysm when ruptured can cause life-threatening complications like
- Internal bleeding
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Stroke
- death
Causes
Sometimes Aneurysms are present at birth. Other times they develop over time due to various etiological factors. Some of the causes are
- Narrowing of the blood vessels also known as atherosclerosis
- Genetics (family history)
- Hypertension
- An aortic injury due to any reason
Risk Factors
Different people are at risk of developing different types of aneurysms. Abdominal aneurysms are more common in the male population than in females. People above the age of 60 and those who are chain smokers are at risk of developing any type of aneurysm.
One study suggests they are more common in the white population but they can occur in any race.
Diagnosis
Routine checkups and regular screening are important because it helps in the diagnosis of unruptured aneurysms which are otherwise asymptomatic.
Symptoms of ruptured aneurysms can be confirmed by the following tests
- CT scan
- CT or MRI angiography
- ultrasonography
Treatment
Unruptured aneurysms are monitored closely by your doctor.
The treatment depends on the location, size, and type of aneurysm. Sometimes medications can be given but the other times, surgery is needed. If an aneurysm is large, the following procedures can be performed
- Endovascular Aneurysm repair (EVAR)
A catheter is passed to repair the artery with the help of a graft. If an abdominal aneurysm has to be repaired, it is known as Thoracic Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (TEVAR) and if a custom graft is prepared with customized openings, it is called a Fenestrated endovascular aneurysm graft (FEVAR).
- Open surgery to remove the aneurysm via incision
- Cerebral aneurysms can be treated by endovascular coiling
- A brain surgery called microvascular clipping where a clip is placed at the base of the artery to cut the blood supply
- Catheter embolization to cut the blood supply to the aneurysm and a tube is placed to stop bleeding by medication or embolism.

What is a False Aneurysm?
Definition
An injury to the wall of a blood vessel that leads to the pooling of blood in the surrounding tissues is called a pseudo aneurysm or false aneurysm.
Symptoms
A false aneurysm might go undetected and appear asymptomatic.
Some of the uncommon symptoms are:
- A small lump underneath the skin which can be throbbing or pulsating
- The lump area can be tender to touch
- Texture of the skin involved can change
- Bruising
- A mass pressing the nerve can cause numbness or tingling sensation
Causes
There are two main causes of a pseudo aneurysm
- Iatrogenic
- Non-iatrogenic
Iatrogenic means when a false aneurysm is caused as a result of any surgery or medical procedure, for example when a catheter is inserted in the femoral artery, failure in anastomosis of veins, complications in cardiac catheterization, etc.
Non-iatrogenic causes are trauma, any infection, and pancreatic fistula caused as a result of pancreatitis.
Risk Factors
Some people are at more risk of developing a pseudo aneurysm. The common risk factors are
- Patients taking antiplatelet medications
- On anticoagulants or blood thinning medicines
- A small rupture or injury below the femoral artery
Diagnosis
- History
- Physical examination
- Duplex ultrasonography
- CT Angiography
- CT abdomen
Treatment
A small pseudo aneurysm is usually kept under observation and is monitored for its size and characteristics.
A pseudo aneurysm more than 2 cm in diameter might need one of the following treatments
- Compression repair guided by ultrasound which helps release the build-up blood by applying pressure at the site
- Medicine delivery guided by ultrasound which enables injection of thrombin in the pseudo aneurysm.
- Surgery is required if ultrasound-guided techniques don’t work.
Differences between Aneurysm and False Aneurysm
Definition
A slight bulge in the wall of an artery due to weakening of the wall is called an aneurysm. While pseudo aneurysm is the pooling of blood in the surrounding tissues due to a ruptured or injured artery wall.
Causes
An aneurysm develops as a result of conditions like atherosclerosis, family history, injury of the aorta, or high blood pressure. While a pseudoaneurysm is either due to a complication of previous surgery, an infection, trauma, or conditions like pancreatitis.
Symptoms
An aneurysm is asymptomatic when unruptured. Once ruptured, it can cause lightheadedness, confusion, blurred vision, slurred speech, sharp headache, sudden pain in the chest, tachycardia, etc. A pseudo aneurysm can be found as a pulsating, painful mass under the skin, which can change the texture of the skin and can cause bruising.
Risk Factors
People at risk of developing aneurysms are smokers, above sixty years of age, males, and the white population. While pseudoaneurysm occurs in people taking anticoagulants, antiplatelet, and people with an injured femoral artery.
Diagnosis
CT and CTA are the most reliable in the diagnosis of an aneurysm. Duplex ultrasonography is the gold standard in pseudo aneurysm.
Treatment
Medication and surgery are treatments of choice in both true aneurysms and false aneurysms.
Surgical techniques are different according to location.
Table comparing Aneurysm and False Aneurysm
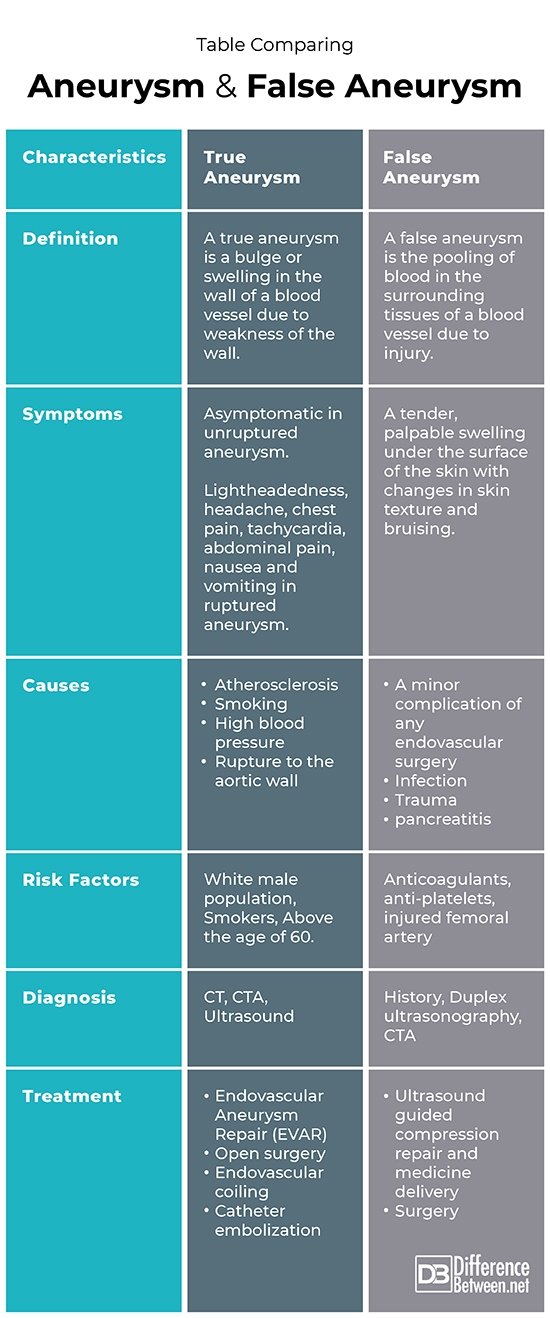
Summary of Aneurysm and False Aneurysm
- A bulge in the wall of weakened artery due to blood is a true aneurysm while pooling of blood in the surrounding tissues due to injured arterial wall is false aneurysm.
- Aneurysm is more prevalent in people suffering from hypertension, of old age, smokers while a pseudo aneurysm is prevalent in people taking anticoagulants, antiplatelet and those having an injured aorta.
- Aneurysm presents as lightheadedness, confusion, headache, abdominal pain, sharp and sudden chest pain when ruptured while pseudo aneurysm presents as a soft, palpable swelling under the surface of skin which is tender to touch.
- Aneurysm can become life-threatening and even fatal if ruptured while pseudo aneurysm does not pose potential threat to life and can be kept under observation.
- Aneurysm is treated by surgical procedures like Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR), microvascular clipping, catheter embolization etc. while pseudo aneurysm is either kept under observation and resolves on its own or treated by procedure like ultrasound guided compression repair, ultrasound guided medicine delivery and even surgery.
FAQs
What is the difference between a true aneurysm and a false aneurysm?
A true Aneurysm is a bulge or swelling in the arterial wall due to soft walls and a pseudo aneurysm is a blood pool in the surrounding tissues because of injured vessels.
What is the difference between false aneurysm and dissection?
When all three walls of blood vessels are ruptured and blood pool forms in the surrounding tissues, this is called false aneurysm. While when only inner part of the wall of blood vessel is injured, it is called a dissection.
What are the 3 types of aneurysms?
Three main types of aneurysms are
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Cerebral aneurysm
- Thoracic Aortic aneurysm
How serious is a pseudo aneurysm?
Most of the times, pseudo aneurysms are not serious and can go away on their own. Very rarely they can grow and rupture, only then they become life threatening.
What is an example of a false aneurysm?
Examples of false aneurysms are visceral, femoral and aortic pseudo aneurysms.
What is a false aneurysm called?
A false aneurysm is also called pseudo aneurysm.
- Difference Between Cystocele and Rectocele - September 8, 2023
- Comparison Between DHEA and DHEA Sulfate - September 1, 2023
- Difference Between Osteoporosis and Osteopenia - June 14, 2023
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Riveria, P. A., & Dottily, J. B. (2022, March 9). False aneurysm. False Aneurysm - an overview | Science Direct Topics. Retrieved January 21, 2023, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542244/
[1]NSakalihasan MD, a, ProfR Limet MD, ODDefawePhD, & Summary Abdominal aortic aneurysms cause 1·3% of all deaths among men aged 65–85 years in developed countries. These aneurysms are typically asymptomatic until the catastrophic event of rupture. Repair of large or symptomatic aneurysms by open surgery or e. (2005, April 29). Abdominal aortic aneurysm. The Lancet. Retrieved January 21, 2023, from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0140673605664598
[2]Dor, V., Saab, M., Coste, P., Kornaszewska, M., & Montiglio, F. (2008, May 7). Left ventricular aneurysm: A new surgical approach. The Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgeon. Retrieved January 21, 2023, from https://www.thieme-connect.com/products/ejournals/abstract/10.1055/s-2007-1013899
