Difference Between Coronary Artery Disease and Congestive Heart Failure
What is Coronary Artery Disease:
Coronary artery disease is caused by plaque accumulation in the walls of the arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the heart (called coronary arteries). Plaque is made up of cholesterol. Plaque build-up causes arteries to keep narrowing with time. This process is known as atherosclerosis.
Symptoms:
It is usually symptomatic or unnoticeable in the early stages but later the symptoms are:
- Angina- chest pain mostly occurs in the centerfire or left side of the body and often radiates to the left shoulder and left arm. Anxiety often aggravates chest pain/angina
- Shortness of breath leads to difficulty in breathing.
- Fatigue(tiredness) happens when the body does not deliver enough blood to the organs of the body.
- Sweating
- Heart attack- a completely blocked coronary artery can lead to a heart attack, in a few cases, attacks do not show up any symptoms and are sudden and silent.
Risk Factors of Coronary Artery Disease:
- Family history increases the risk of Coronary artery disease (CAD). Other causes are discussed below
- Increasing age cause the vessels to become narrow and weak (more permeable to cholesterol)
- High uncontrolled blood pressure is one of the leading causes
- High serum cholesterol levels
- Obesity
- Lack of physical activity/exercise
- An unhealthy diet having an intake of junk food
- Smoking, tobacco, and alcohol
All these causes lead to high cholesterol levels in the body which after circulating into the blood start accumulating in the cardiac vessels as they are narrowly leading to CAD.
Treatment
There are many ways to diagnose disease including Electrocardiogram (ECG) exercise stress test and many more. Once it is diagnosed then the treatment options are as below:
Medical Treatment:
It is mostly tried to treat through lifestyle changes. Eating healthy is advised with less cholesterol consumption, quitting, smoking, and adequate exercise.
- Medicines needed to treat CAD are cholesterol drugs needed to break up plaque deposits and lowering down cholesterol in the blood. Aspirin is a blood thinner so blood may circulate through the vessel without any obstruction.
- Beta-blockers slow the heart rate. They also help in reducing blood pressure. If you’ve ever had a heart attack, beta-blockers may reduce the risk of future attacks.
- Calcium channel blockers, in cases where beta blockers are not recommended, are advised.
- ACE inhibitors help in reducing blood pressure as well.
- Nitro-glycerine is the medicine of choice in cases of emergencies. It helps in instant widening the vessels if kept in the mouth and helps in reducing chest pain. It is available in the form of a pill, spray, or patch.
Surgical Treatment:
- Coronary angioplasty and stent placement. This procedure is done to open clogged heart arteries. It is called percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Cardiologist guides a thin, flexible tube (catheter) to the narrowed part of the heart artery, then a tiny balloon is inflated to help widen the blocked artery and improve the blood flow. A small wire mesh (stent) is placed in the artery during angioplasty which helps in keeping the artery open. Stent also lowers the risk of repetitive artery narrowing.
- Coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG). A surgery is performed in which a healthy blood vessel is taken from another part of the body to create a new path for blood in the heart. CABG is open-heart surgery. It is usually done only in cases with several many narrowed heart arteries.

What is Congestive Heart Failure?
Congestive heart failure is a long-term condition that happens when the heart does not pump enough blood to give the body a normal supply because of which blood and fluids start accumulating in the lungs and legs over time.
Causes:
- Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common cause of heart failure. The disease results from the build-up of fatty/plaque deposits into the arteries causing narrowing. This reduces blood flow and can lead to a cardiac attack.
- Hypertension/high blood pressure.
- Inflammation of the heart muscles is called myocarditis. Myocarditis is most commonly caused by a virus including the COVID-19 virus and can lead to left-sided heart failure.
- Arrhythmias are irregular heart rhythms causing the heart to beat fast leaving an extra load on the muscles.
- Other chronic diseases such as diabetes, HIV infection, or hyper/hypothyroidism can lead to heart failure.
Symptoms:
Congestive heart failure symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath/difficulty in breathing especially at night or when lying flat.
- Chest pain/angina
- Heart palpitations.
- Fatigue when you’re active.
- Swelling in your ankles, legs, and abdomen. This is due to fluid accumulation called edema
- Weight gain.
- Need to urinate again and again while resting at night.
- Dry cough.
- Fluid accumulation in the stomach is also known as ascites.
- Loss of appetite or stomach upset (nausea).
Treatment:
Medical Treatment:
- Lifestyle Changes are advised like coronary artery disease. Other than those, salt consumption is strictly prohibited because salt helps in fluid retention within the body. Caffeine
- Vasodilators expand the blood vessels, ease blood flow, and reduce blood pressure.
Surgical Treatment:
In more severe cases, surgery is required to bypass blocked arteries or to replace heart valves. In a few cases, a pacemaker called biventricular pacing therapy is done which helps both sides of the heart work properly or an implantable cardioverter defibrillator is advised which shocks the heart into converting a potentially fatal fast rhythm to a normal one. Ventricular assist devices (VAD therapy) may be used as an aid to heart transplantation.
Table Comparing Coronary Artery Disease and Congestive Heart Failure
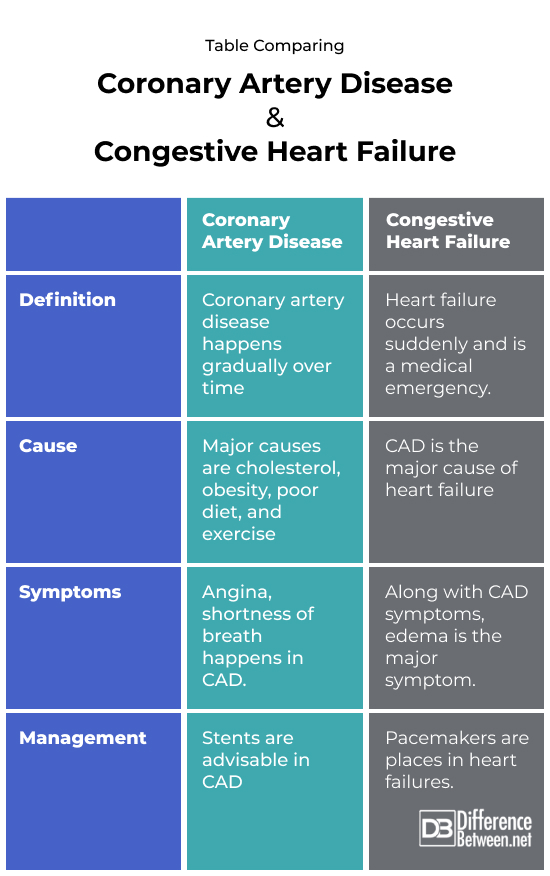
Summary of Differences between Coronary Artery Disease and Congestive Heart Failure:
If summarized, Coronary artery disease is used to describe what happens when the heart’s blood supply is blocked or interrupted by the accumulation of fatty substances in the coronary arteries. With time, the walls of your arteries can be filled with fatty deposits. Whereas heart failure occurs when the heart muscles do not pump blood properly. When this happens, blood often goes back and fluid can build up in the lungs, causing shortness of breath and leading to heart failure.
FAQs
Is congestive heart failure a coronary artery disease?
Heart failure is caused by many conditions that damage the heart muscles among which is Coronary artery disease where the vessel is blocked by fatty deposits inhibiting proper blood flow to the other cells of the body
What is the difference between heart disease and congestive heart failure?
The major difference is heart disease is chronic and develops over time whereas heart failure is suddenly causing a medical emergency.
Can you have congestive heart failure without coronary artery disease?
Heart failure can also be due to non-ischemic cardiomyopathy where cardiac muscles weaken to pump the blood rather than clog. So this could be the reason for heart failure as well other than CAD.
What are the 4 types of heart left-sidedLeft-sided heart failure?
- Right-sided heart failure
- Diastolic heart failure
- Systolic heart failure
What are the 3 types of coronary heart disease?
- Obstructive coronary artery disease.
- Nonobstructive coronary artery disease.
- Spontaneous coronary artery dissection.
- Difference Between Cystocele and Rectocele - September 8, 2023
- Comparison Between DHEA and DHEA Sulfate - September 1, 2023
- Difference Between Osteoporosis and Osteopenia - June 14, 2023
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. (2022, May 25). Coronary artery disease. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved April 16, 2023, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/coronary-artery-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20350613
[1]Congestive heart failure: Prevention, treatment, and research. Congestive Heart Failure: Prevention, Treatment, and Research | Johns Hopkins Medicine. (2022, April 8). Retrieved April 16, 2023, from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/congestive-heart-failure-prevention-treatment-and-research
[2]WebMD. (n.d.). Congestive heart failure: Symptoms, causes, treatment, types, stages. WebMD. Retrieved April 16, 2023, from https://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/guide-heart-failure
