Difference Between Gestational Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a blood sugar problem that is diagnosed or develops during pregnancy. Type 2 diabetes is the condition in which blood sugar problems occur in adulthood, most often after age 40.
What is Gestational Diabetes?
Definition:
Gestational diabetes mellitus is a condition of insulin resistance that develops during pregnancy or is first diagnosed when a woman is pregnant. The condition is a complication in about 7% of all pregnancies. The diabetes also seems to develop most often between weeks 24 to 28 of a pregnancy.
Causes:
It is thought that gestational diabetes is due to hormonal changes that take place during pregnancy which, in some cases, leads to insulin resistance. Women who are obese are also more likely to develop the condition during pregnancy; however genetics may also play a role and thus some women may already be predisposed to the condition.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis is best done based on the results of an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). A blood measure at 1 hr giving a blood glucose value of between 130 and 140 mg/dl and also a similarly high value at 3 hrs in the OGTT test would indicate the presence of diabetes. Sometimes a single test measuring blood glucose can be done either randomly or after a period of fasting. A random blood glucose level of greater than 200 mg/dL, or a fasting value at or greater than 100 mg/dL are both indicative of diabetes.
Symptoms:
Many women with gestational diabetes do not have any obvious symptoms. However, symptoms that may occur include unusual thirst and increased urination, as well as feeling unusually tired.
Treatment:
Often a change in diet along with exercise can help to control the diabetes, but in other cases the doctor may suggest that the person have insulin injections or take oral medication. The drug glyburide is often used for treating gestational diabetes. Extra monitoring of the developing fetus is often recommended after a diagnosis of gestational diabetes.
Complications:
The main complication of gestational diabetes is that the baby may be affected and be born with jaundice or with blood sugar problems. The other complication is that it raises the risk of the women developing type 2 diabetes in later years.

What is Type 2 diabetes?
Definition:
Type 2 diabetes is a disease that develops in people in which cells become resistant to the effects of the hormone insulin leading to abnormally high blood sugar levels.
Causes:
Type 2 diabetes is caused by cells of the body becoming resistant to the effects of the hormone insulin which acts to remove glucose from the blood and allow it to enter cells of the body. The cause of type 2 diabetes appears to be a combination of genetics and lifestyle factors. Certain genes are suspected to be involved. Being obese and having a waist that is greater than 25 to 40 inches seem to also be associated with development of the condition. Having a poor diet and living a sedentary life and being older than age 40 also seem to be associated with the development of type 2 diabetes.
Diagnosis:
The best test for diagnosis is the oral glucose tolerance test although a fasting blood glucose value above 100 mg/dL can indicate diabetes. An OGTT value between 140 and 199 mg/dL can indicate pre-diabetes, and above 200 mg/dL is considered a positive result for diabetes.
Symptoms:
Type 2 diabetes has notable symptoms including problems with eyesight, feeling very tired, feeling unusually hungry and thirsty. Urinating more often and also having nausea and unusual fatigue are also symptoms of type 2 diabetes. People can sometimes have a fruit-like smell to their breath if the condition is badly controlled.
Treatment:
Sometimes patients are prescribed the drug metformin, but in many cases a change in diet and increase in exercise can treat the condition.
Complications:
The high blood sugar levels damage many organs of the body and so complications include nerve damage leading to loss of eyesight, gangrene resulting in limbs being amputated, and problems with the heart and kidneys. People can die as a result of type 2 diabetes.
Difference between Gestational diabetes and Type 2 diabetes
Definition
Gestational diabetes is blood sugar problems that occur and are diagnosed for the first time during pregnancy. Type 2 diabetes is the condition in which there are blood sugar problems that occur in adulthood with blood sugar being too high.
Gender affected
Gestational diabetes only affects pregnant women. Type 2 diabetes affects both men and women, most commonly over age 40.
Causes
The cause of gestational diabetes is mainly hormonal changes of pregnancy but genetics and poor diet can have an effect. The cause of type 2 diabetes is thought to be a combination of genetics, poor diet, obesity, and lack of exercise.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of gestational diabetes can be made if the values of the oral glucose tolerance test values are between 130 and 140 mg/dL or the fasting blood glucose is 100 mg/dL or more. Diagnosis of type 2 diabetes can be made if the values of the oral glucose tolerance test values are 200mg/dL or more and the fasting blood glucose is above 100 mg/dL.
Symptoms
There may be no symptoms of gestational diabetes or else people may feel thirsty, urinate often and feel tired. The symptoms of type 2 diabetes include hunger, thirst, urinating more often, feeling tired and also having a fruit-like smell to the breath.
Treatment
Gestational diabetes can be treated with insulin injections or oral glyburide if needed, else by exercise and diet. Type 2 diabetes can sometimes be treated simply by a change in diet and exercising, else metformin may be prescribed.
Complications
There are complications associated with gestational diabetes such as an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life; the newborn child may have jaundice and blood sugar issues. Complications associated with type 2 diabetes include nerve damage leading to kidney and heart problems, loss of vision, and gangrene leading to limb amputation, and even death.
Table comparing Gestational diabetes and Type 2 diabetes
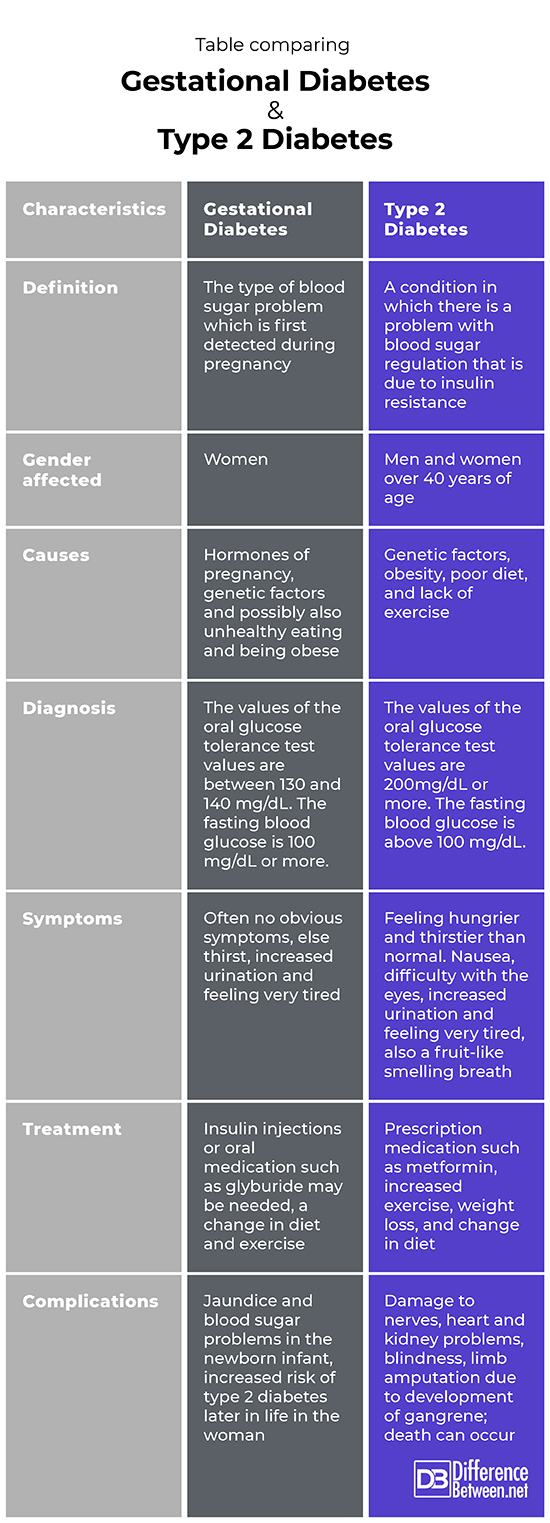
Summary of Gestational diabetes Vs. Type 2 diabetes
- In both gestational diabetes and type 2 diabetes blood sugar levels are badly regulated so that blood sugar is too high.
- Gestational diabetes is only diagnosed in pregnancy and can pose a risk to the newborn child.
- Type 2 diabetes occurs usually after about age 40, and can be controlled sometimes by a change of diet and by increasing exercise.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Type_2_Diabetes_(28081593711).jpg
[1]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Gestational_diabetes_kit.jpg
[2]American Diabetes Association. "Gestational diabetes mellitus." Diabetes care 27.suppl 1 (2004): s88-s90.
[3]Brutsaert, Erika F. “Diabetes.” Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders”. Merck & Co., 2018, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/endocrine-and-metabolic-disorders/diabetes-mellitus-and-disorders-of-carbohydrate-metabolism/diabetes-mellitus-dm
[4]Friel, Lara A. "Diabetes mellitus in pregnancy". Merck & Co., 2019, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/gynecology-and-obstetrics/pregnancy-complicated-by-disease/diabetes-mellitus-in-pregnancy?query=gestational%20diabetes

My son was diagnosed diabetes 2008. He is in his late 30’s. He urinate a lot, usually during the night and his blood sugar was 600. I do not know where he could have inherited it. Since then I have worked on finding a good way to control it or reverse it. and I was introduced to Akanni Herbal Centre and ever seem My son started using diabetes herbal formula I purchased online from AKANNI HERBAL CENTRE November last year. After 5 weeks of usage, his diabetes was totally reversed, blood sugar now normal and his last A-1C was 4.0 perfect. To know more about AKANNI HERBAL CENTRE visit www. akanniherbalcentre .com