Difference Between Headache and Concussion
What is Headache and Concussion?
Both conditions are associated with head. However, headache is a constant pain in head that may be caused due to several factors and concussion is a traumatic brain injury that prevents the brain to function properly. Headache is one of the symptoms of concussion.
Severity of concussive injury is closely related to the development of chronic headaches. Concussions and headaches have few common symptoms like dizziness, nausea, vomiting, poor concentration, fatigue and personality changes like depression or nervousness, sensitivity to light and noise.
What is a Headache?
A headache involves pain in the head that could arise from many disorders or may be a disorder in and of itself. There major types of headaches include; tension (muscular contraction headache), sinus (rhinosinusitis), migraine (vascular headaches) and cluster headaches (suicide headaches).
Headaches may result from the dilation of the blood vessels (the flow of blood increases because of decrease in vascular resistance and upsurge in cardiac output) in the head; tightening or shortening of the muscles (activation of tension-generating sites within muscle fibres) of the scalp, face or neck; or brain swelling that stretches the brain coverings.
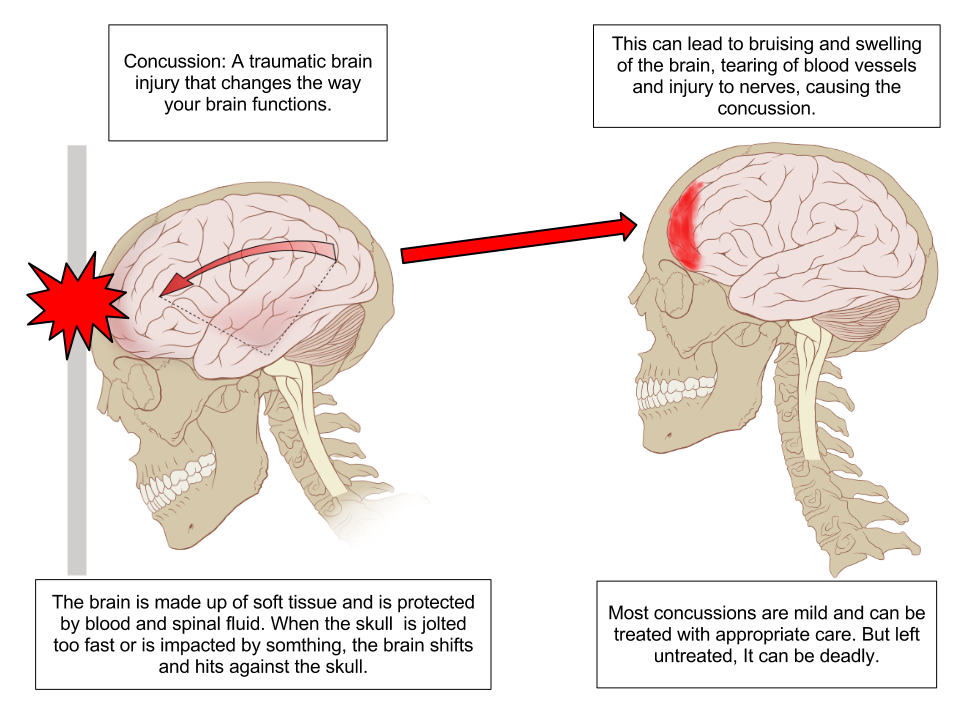
What is a Concussion?
A concussion is a type of brain injury that temporarily stops the brain functions. It is commonly described as “getting your bell rung” and seeing stars. These casual terms may make the condition sound minor, but concussions are serious and can even be deadly.
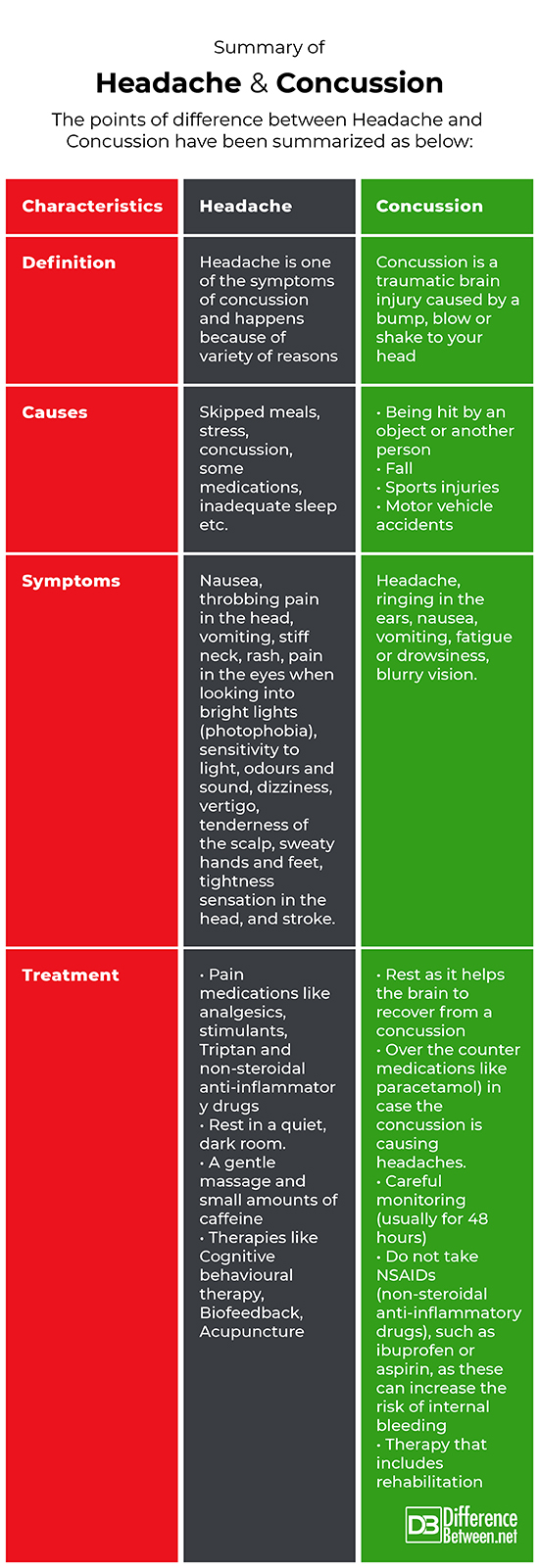
Difference between Headache and Concussion
Definition
Headache
It is defined as a continuous pain in the head or the upper neck. Headaches are caused due to numerous reasons. Common causes are lack of sleep, false eyeglass prescription, anxiety and emotional distress and stress, and loud noise. It usually needs self-treatment and can be treated by taking medicines alike aspirin, paracetamol and ibuprofen.
Concussion
It is also called – MTBI (Mild Traumatic Brain Injury). It is a type of mild brain injury that is caused due to a mild blow to the head. It results in temporary cognitive symptoms which are temporary. A headache is one of the symptoms of a concussion that doesn’t go with painkillers.
There is no specific treatment for a concussion. Complete rest and restricted activities help in the recovery of the brain.
Types
Headache
Types include;
- Migraine headaches
- Stress headaches
- Tension headaches
- Sinus headaches
- Anxiety
- Headaches caused by digestive problems
- Headaches caused due to brain injury or brain disease (for example any brain surgery and concussions)
Concussion
Types include;
- Mild (grade 1) – symptoms last for less than 15 minutes.
- Moderate (grade 2) – signs and
- symptoms last for longer than 15 minutes.
- Severe (grade 3)- person loses consciousness
Another categorization identified by the symptoms they exhibit include;
- Vestibular (balance issues)
- ocular (vision issues)
- Mood and anxiety
- Migraine headaches
- Cervical (issues with the neck)
Symptoms
Headache
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Blind spots, Bright flashing dots or lights, wavy or jagged lines (aura)
- Photophobia (eye pain because of looking into bright lights)
- Dizziness
- Sensitivity to noise, light
- Paleness
- Vertigo
- Loss of appetite
- Tenderness of the scalp
- Difficulty falling asleep and staying asleep
- Tightness sensation in the head, and
- Stroke
- Disturbed concentration
Concussion
Physical symptoms include;
- Nausea feeling
- Puking
- Headache
- Ringing sound in the ears
- Drowsiness or tiredness
- Blurred vision
- Amnesia
- Dizziness
- Mind feels confused and a feeling of walking in a fog
Some other person or a witness may see the below given symptoms in the person suffering from concussion;
- Temporary loss of consciousness (happens rarely)
- Slurred (poor pronunciation of words) speech
- Person takes longer time to respond to any questions
- Forgetfulness
- Dazed appearance
Some symptoms happen instantly, and some happen days after the brain injury, like;
- Disturbed sleep
- Depression
- Loss of focus and concentration
- Crankiness and irritation
- Memory complaints
- Sensitivity to loud noise and light
- Disorders of smell and taste
Causes
Headache
- Bacterial Infection (Interior or exterior of the head)
- Cluster Headache (Headaches that occur in patterns or clusters)
- A cold-stimulus headache or Brain Freeze (Cold Drink or ice-cream headache)
- Compression of Head (Hat, Helmet, etc.)
- Hyperventilation (a condition in which you start to breathe very fast)
- Illicit Drug Withdrawal (illicit substances that either stimulate (like cocaine) or inhibit (like heroin) the central nervous system or cause hallucinogenic effects (like marijuana)
- Intracranial Haemorrhage (a type of bleeding that occurs inside the skull -cranium).
- Medications (Both Prescription and Non-prescription (over-the-counter)
- Sexual Activity
- Trauma Injury to neck or head
- Viral Infection (Interior or exterior of the Head)
Concussion
Common causes of concussions include;
- Automobile accidents
- Falls
- Slurred speech
- Horseback riding accident
- Excessive vomiting
- Sports injuries
- Cycling accidents
- Assaults
- Extreme tiredness
- Playground accidents
- Seizures or convulsions
- Explosions
- Being hit by an object or another person
Summary
The points of difference between Headache and Concussion have been summarized as below:
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Eckner, J. T., Seifert, T., Pescovitz, A., Zeiger, M., & Kutcher, J. S. (2017). Is migraine headache associated with concussion in athletes? A case-control study. Clinical journal of sport medicine: official journal of the Canadian Academy of Sport Medicine, 27(3), 266.
[1]Lords, Q., & Greene, J. P. (2014). Traumatic migraine versus concussion: a case report. Sports health, 6(5), 406-409.
[2]Schwedt, T. J., Chong, C. D., Peplinski, J., Ross, K., & Berisha, V. (2017). Persistent post-traumatic headache vs. migraine: an MRI study demonstrating differences in brain structure. The journal of headache and pain, 18(1), 87.
[3]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Concussion_Anatomy.png
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Headache.png
