Difference Between Alpha Lipoic Acid and R-Lipoic Acid
Alpha lipoic acid (ALA) is known as 1,2-dithiolane-3-pentanoic acid. It has two enantiomers: RLA and SLA. The r-lipoic acid (RLA) is one of the enantiomers of alpha lipoic acid.
What is Alpha Lipoic Acid?
Definition:
Alpha lipoic acid (ALA), also known as 1,2-dithiolane-3-pentanoic acid is a compound that contains sulfur along with atoms of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. It includes both the unnatural enantiomer that is known as the s-lipoic acid (SLA) and the natural enantiomer that is known as the r-lipoic acid (RLA).
Formation:
The natural form of alpha lipoic acid, the RLA, is formed naturally through chemical reactions that take place in the cells within the body of plants and animals. The SLA enantiomer is formed in the laboratory by means of various chemical reactions that first took place in the 1950s. Scientists were able to modify and transform the natural form of ALA to form the mirror image or enantiomer, which became known as the s-form, the SLA.
Function:
Alpha lipoic acid has an important function in the mitochondria of cells where reactions that involve dehydrogenase enzymes take place. It also seems to help prevent damage to membranes through its interaction with glutathione and ascorbic acid, and it also functions as a strong antioxidant.
Health Benefits:
There have been many claims regarding the benefits of alpha lipoic acid to a persons’ health. There is, in fact, some scientific evidence that does support such claims. In fact, researchers have found that alpha lipoic acid has been shown to help in situations of neural degeneration and for difficulties that diabetics have; particularly in cases of diabetic neuropathy. It also seems to help in cases where there is ischemia-reperfusion injury, in other words where tissue has been without blood and oxygen which is then later restored.
What is R-Lipoic Acid?
Definition:
The r-lipoic acid (RLA) is the natural form of the compound known as alpha lipoic acid. This is one of two enantiomers of the alpha lipoic acid compound.
Formation:
The r-lipoic acid is formed through a series of reactions that take place in the mitochondria from the molecule octanoic acid. The enzyme octanoyltransferase is involved in further modifying the molecule so that it attaches to a lipoyl protein. The lipoyl synthase enzyme then functions to replace some of the hydrogens in the molecule with sulfur atoms. The final product that is formed stays attached to a protein.
Function:
The r-lipoic acid occurs in cells bound to protein molecules. It functions as a cofactor and assists in metabolic reactions that involve α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and pyruvate dehydrogenase where it helps bind acyl groups during the metabolic process. It can be reduced to dihydrolipoic acid which is a strong antioxidant.
Health benefits:
Studies have indicated that the r-lipoic acid form of alpha lipoic acid is very beneficial for health. It was actually shown to decrease some of the effects of aging when studies in rats in the laboratory. In fact, it stopped the loss of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and glutathione in the liver cells, which usually occurs with aging. It also increased the ability of rats to take in and use oxygen, another reversal of something commonly evident in aged individuals.
Difference between Alpha Lipoic Acid and R-Lipoic Acid?
-
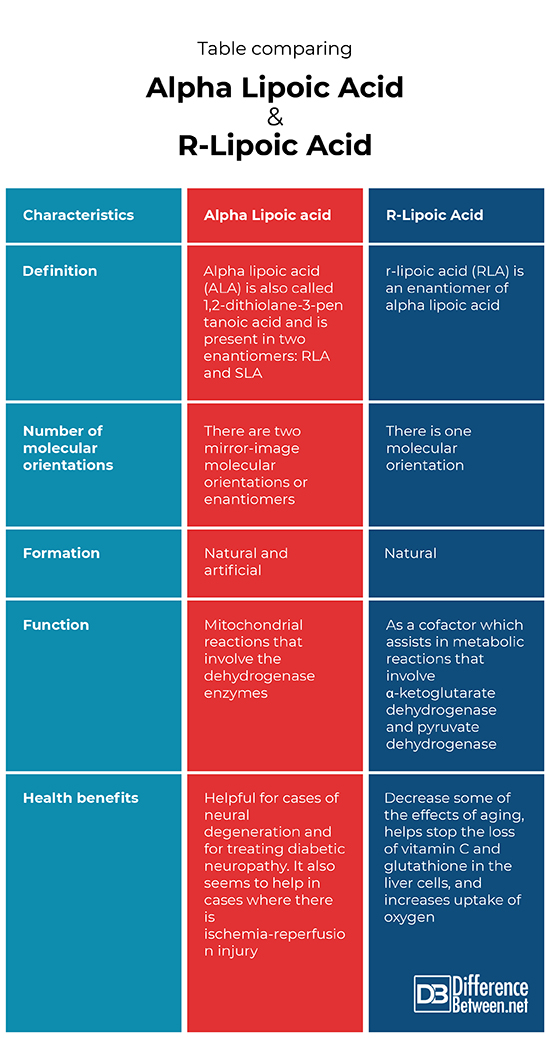
Definition
Alpha lipoic acid (ALA) is also known as 1,2-dithiolane-3-pentanoic acid. It is also present in the form of two enantiomers: RLA and SLA. The r-lipoic acid (RLA) is one of the enantiomers of alpha lipoic acid.
-
Number of Molecular Orientations
The alpha lipoic acid occurs in at least two different molecular orientations as RLA and SLA. The r-lipoic acid only occurs in the form of one molecular orientation.
-
Formation
The alpha lipoic acid formation varies depending on what form it is in. In fact, it is formed either naturally inside the mitochondria of cells or is artificially created by scientists. The r-lipoic acid is the form of alpha lipoic acid that is formed in the mitochondria from octanoic acid involving various enzymes.
-
Function
The function of alpha lipoic acid is to help with various chemical reactions that involve the dehydrogenase enzymes, which occur in the mitochondrion. The function of r-lipoic acid specifically is as a cofactor that helps in metabolic reactions that involve α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and pyruvate dehydrogenase
-
Health Benefits
The alpha lipoic acid appears to help in situations where a person has neural degeneration and it is helpful for diabetics. It is of particular use in helping treat diabetic neuropathy. It also aids in situations where there is an ischemia-reperfusion injury. The r-lipoic acid helps prevent some of the effects of aging such as the loss of the amino acid glutathione, and vitamin C from the liver. It also helps to improve the use and uptake of oxygen by cells.
Table comparing Alpha Lipoic Acid and R-Lipoic Acid
Summary of Alpha Lipoic Acid Vs. R-Lipoic Acid
- Alpha lipoic acid consists of two forms or enantiomers.
- The r-lipoic acid is the natural form in which alpha lipoic acid occurs and is made in organisms.
- The s-lipoic acid is an unnatural form of the alpha lipoic acid which has been chemically synthesized by people.
- The r-lipoic acid is formed naturally in the mitochondria of living plant and animal cells.
- The s-lipoic acid was actually synthesized by scientists in the laboratory in the 1950s.
- Alpha lipoic acid and r-lipoic acid both have many health benefits.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Hagen, Tory M., et al. "(R)-α-Lipoic acid-supplemented old rats have improved mitochondrial function, decreased oxidative damage, and increased metabolic rate." The FASEB Journal 13.2 (1999): 411-418.
[1]Packer, Lester, Eric H. Witt, and Hans Jürgen Tritschler. "Alpha-lipoic acid as a biological antioxidant." Free radical biology and medicine 19.2 (1995): 227-250.
[2]Shay, Kate Petersen, et al. "Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential." Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects 1790.10 (2009): 1149-1160.
[3]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/7/7c/AlphaLipoicAcid.jpg
[4]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/1b/%28RS%29-Lipoic_Acid_Structural_Formulea_V.1.svg/500px-%28RS%29-Lipoic_Acid_Structural_Formulea_V.1.svg.png
