Difference Between Gingivitis and Periodontitis
Gingivitis and Periodontitis are both periodontal diseases. The major difference between the two is that gingivitis is reversible, while periodontitis is not.
The reason for that is that there is permanent damage and loss of bone in periodontitis, that cannot be recovered. The complications include tooth loos, increased risk for diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, asthma and coronary artery disease. If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress and spread to the underlying bone and tissue and can result in periodontitis.
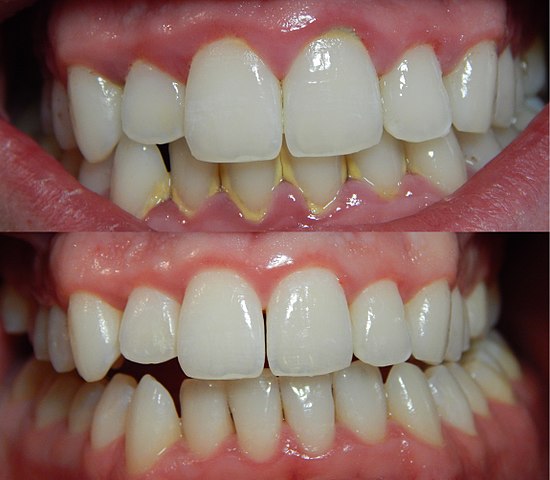
What is Gingivitis?
The gingiva term is used for the gums i.e. the visible mucosa around the teeth. It is a mild form of gum disease that causes redness, irritation and inflammation in the gums. The most common cause of this disease is poor oral hygiene. Good oral hygiene habits like brushing twice a day, regular dental check-ups, regular flossing and use of mouthwash can help, prevent and reverse gingivitis.
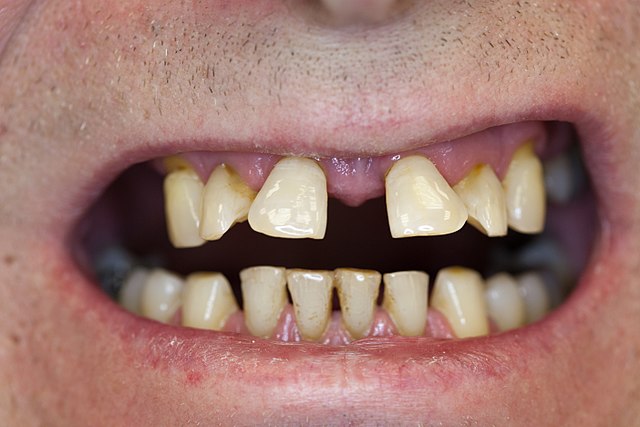
What is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis is an advanced stage of gum disease where the gums are seriously infected and the disease can damage the gums and the jaw bone permanently. Periodontitis cannot be reversed. The chronic infection damages the gingiva, soft tissues around the teeth, ligaments and the underlying alveolar bone. It can lead to permanent loss of teeth. Gingivitis (gum inflammation) usually precedes periodontitis (gum disease).
Difference between Gingivitis and Periodontitis
-
Definition
Gingivitis
It is the mild infection of the gums. There is mild inflammation, bad breath and redness involved as well.
Periodontitis
It is a serious gingiva infection that damages the gums and the jawbone permanently. It could lead to permanent loss of teeth.
-
Causes
Gingivitis
- Poor oral hygiene that causes bacteria to build up plaque in the mouth.
- Skin disease, particularly erosive lichen planus
Periodontitis
When gingivitis is not treated in time, it progresses to periodontitis. Bacteria from the plaque enters the bloodstream and damages the gingiva, ligaments and the jaw bones. The untreated gingiva pull farther away from the teeth until a dental probe can fit 3-5 mm deep into the space. The teeth eventually fall out.
-
Symptoms
Gingivitis
Patients with gingivitis may show symptoms like:
- Puffy, swollen and dusky red gums
- Sensitive teeth, tender gums that bleed easily
- Mild foul breath that can go away with proper dental care
Periodontitis
Patients with the more advanced periodontitis may show symptoms like:
- Inflamed, tender, bright red or purplish gums
- Severe receding gums
- Deep periodontal pockets
- Chronic bad breath that doesn’t go away
- Pus between the teeth and the gums
- Misaligned and Loose teeth
-
Treatment
Gingivitis
Treatment for gingivitis includes:
- Descaling which involves deep teeth cleaning to get rid of plaque and tartar
- Brushing teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled brush, dental floss and use of mouthwash
- Fluoride / Triclosan toothpaste (toothpaste which includes a broad spectrum antibacterial ingredient)
- Treatment of underlying conditions
- Professional dental care
Periodontitis
Treatment for periodontitis includes:
Non-surgical treatments
- Scaling
- Root planning
- Antibiotics
Surgical treatments
- Flap Surgery (Pocket reduction surgery)
- Bone and Tissue Grafts
- Gingivectomy -Surgical removal of the gum tissue that is diseased
- Gingivoplasty – Surgical procedure to reshape healthy gum tissue enveloping the teeth.
- Root planning to remove build-up from the roots of the teeth
- Guided tissue restoration
- Tissue stimulating proteins
-
Risk factors
Gingivitis
- Pregnancy
- Chewing or smoking tobacco
- Dry mouth
- Genetics
- Hormonal changes
Periodontitis
- Conditions associated with compromised immune system
- Medications that cause, drug induced gingival overgrowth (For example some calcium channel blockers, cyclosporine)
- Osteoporosis
- Acute diabetes
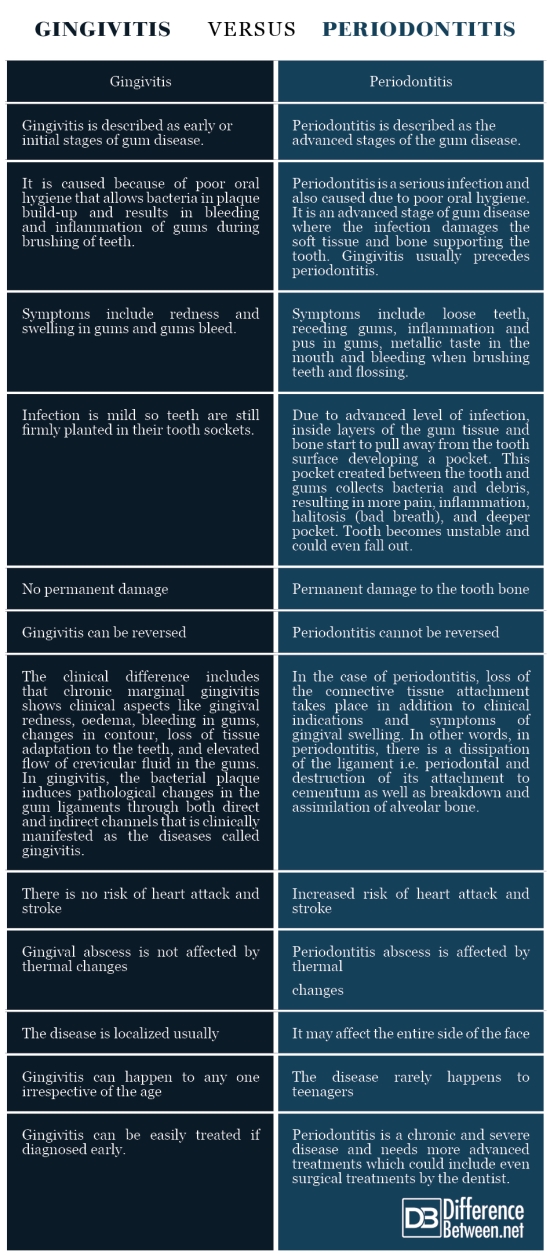
Summary of Gingivitis Vs. Periodontitis
The points of difference between Gingivitis and Periodontitis have been summarized below:
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Hashemipour, M. A., Afshar, A. J., Borna, R., Seddighi, B., & Motamedi, A. (2013). Gingivitis and periodontitis as a risk factor for stroke: A case-control study in the Iranian population. Dental research journal, 10(5), 613.
[1]Pihlstrom, B. L., & Ammons, W. F. (1997). Treatment of gingivitis and periodontitis. Research, Science and Therapy Committee of the American Academy of Periodontology. Journal of periodontology, 68(12), 1246-1253.
[2]Sreenivasan, P. K., Prasad, K. V. V., & Javali, S. B. (2016). Oral health practices and prevalence of dental plaque and gingivitis among Indian adults. Clinical and experimental dental research, 2(1), 6-17.
[3]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/81/Zahnwanderung_wegen_Periodontitis_OK_02.JPG/640px-Zahnwanderung_wegen_Periodontitis_OK_02.JPG
[4]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/ba/Gingivitis-before-and-after-3.jpg/551px-Gingivitis-before-and-after-3.jpg
