Difference Between Immediate and Delayed Hypersensitivity
Immediate hypersensitivity is when an immune reaction to an allergen occurs within a day. Delayed hypersensitivity is when a reaction occurs about 48 hours after being exposed to an allergen.
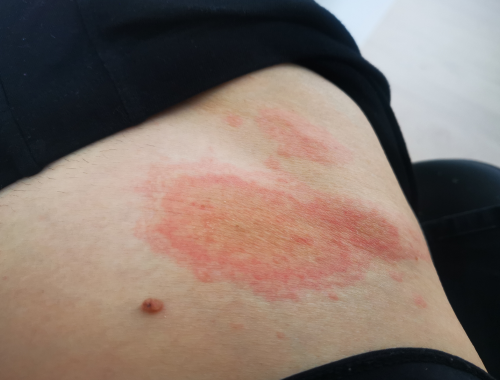
What is Immediate hypersensitivity?
Definition:
This is when there is a heightened immune system reaction within 24 hours to some allergen or protein (antigen) that the body is exposed to.
Causes and prevalence:
Immediate hypersensitivity that is type I, can be due to exposure to certain substances such as foods like peanuts, eggs, or shellfish, or medications such as penicillin. In some people it occurs due to an insect bite or from exposure to parasites like hookworms.
Symptoms and complications:
Symptoms of immediate hypersensitivity include redness of the skin, skin rash with hives, skin itching, runny nose, swelling, coughing, wheezing, and facial flushing. In very severe cases anaphylaxis can occur where swelling of the throat and tongue, dizziness, difficulty breathing, and fainting happens. Anaphylaxis is very dangerous and can lead to death if not treated quickly.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis is based on the patient’s history and symptoms. Confirmation can be done by various immunological tests to allergens. Such tests include skin prick or patch tests.
Treatment:
Treatment depends on the severity of the reaction and includes giving antihistamines; this can be by taking oral medication or done intravenously. Adrenaline may need to be injected into the muscles; especially if the person has an anaphylactic reaction. Giving oxygen may also help.
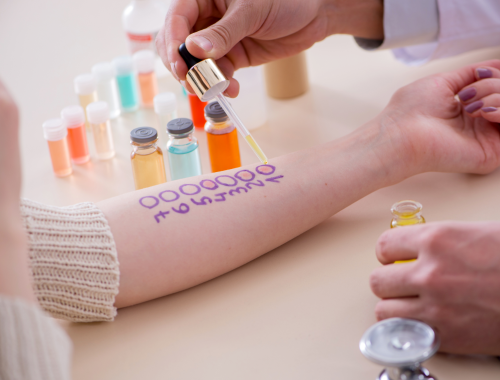
What is Delayed hypersensitivity?
Definition:
Delayed hypersensitivity is an immune system reaction that takes place about 48 hours or longer after exposure to an antigen.
Causes and prevalence:
The causes of the delayed hypersensitivity include certain medications such as antibiotics and anticonvulsants, and some viruses. Contact with certain plants like poison ivy can also cause this reaction to occur.
Symptoms and complications:
Symptoms can include the development of a skin rash, itching, fatigue, and fever. Swelling and wheezing may occur. Contact dermatitis can occur if a person has made contact with some allergen. Certain drug reactions can lead to skin rash with flaking. Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) can occur with certain medications, and can have serious complications, including skin inflammation and infection.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis can be made by the symptoms the patient has and the history of exposure. A skin biopsy and skin patch tests can be done to help diagnose the allergen.
Treatment:
Treatment methods depends on the severity of the problem. Steroid creams can help with the skin rash. A person with SJS may require hospitalization along with antibiotics and fluid therapy.
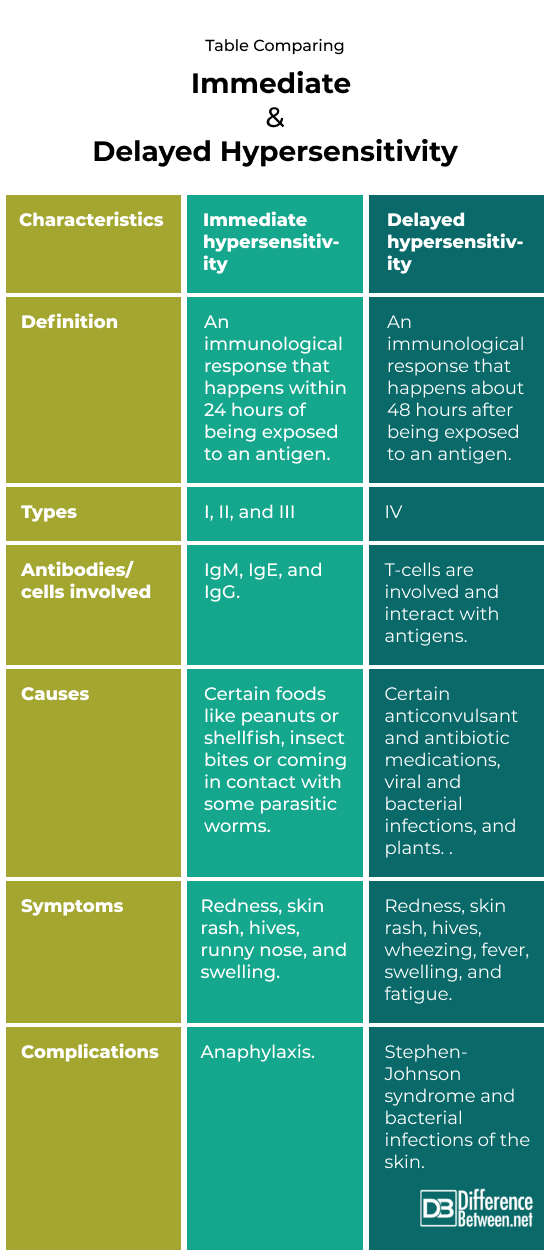
Difference between Immediate and Delayed hypersensitivity?
Definition
Immediate hypersensitivity is an immunological response that happens within 24 hours of being exposed to an antigen. Delayed hypersensitivity is an immunological response that happens about 48 hours after being exposed to an antigen.
Types
Immediate hypersensitivity is classified into one of three types: type I, II, and III. Delayed hypersensitivity is also known as type IV.
Antibodies/cells involved
IgM, IgE, and IgG are the antibodies involved in immediate hypersensitivity reactions. T cells are involved in delayed hypersensitivity reactions.
Causes
The following are potential causes of immediate hypersensitivity: Certain foods like peanuts or shellfish, insect bites or coming in contact with parasitic worms. The following are potential causes of delated hypersensitivity: medications, contact with certain plants, and viral and bacterial infections.
Symptoms
Redness, skin rash, hives, runny nose, and swelling are all symptoms of an immediate hypersensitivity response. Redness, skin rash, hives, wheezing, fever, swelling, and fatigue are signs of a delayed hypersensitivity response.
Complications
Anaphylaxis is a complication of an immediate hypersensitivity response. Bacterial skin infection and SJS are complications of a delayed hypersensitivity response.
Table comparing Immediate and Delayed hypersensitivity
Summary of Immediate Vs. Delayed hypersensitivity
- Immediate hypersensitivity is when the immune system reacts quickly (within 24 hours) to an allergen.
- Delayed hypersensitivity is a reaction of the immune system that only occurs after about 48 hours of exposure to an antigen.
- Certain hypersensitivity reactions can be dangerous and need prompt treatment.
FAQ
What is immediate hypersensitivity?
Immediate hypersensitivity is when the immune system of the person reacts quickly (within 24 hours) upon exposure to an allergen.
What is an example of delayed hypersensitivity?
A good example of delayed hypersensitivity is a person touching poison ivy and developing a skin rash afterward.
What is a delayed hypersensitivity reaction?
A delayed hypersensitivity reaction is when a response from the immune system only occurs later, at 48 hours or more after the person is exposed to the allergen.
Is Type 1 hypersensitivity immediate or delayed?
Type 1 hypersensitivity is an immediate response by the immune system.
What is the most common type of immediate hypersensitivity?
Type I reactions are the most common forms of immediate hypersensitivity, with allergic rhinitis being at the top of the list, occurring in about 22% of people.
Why is it called delayed hypersensitivity?
Delayed hypersensitivity is referred to this way because there is a long delay between the time when you are exposed to an allergen and the time when your symptoms of an allergic response first begin to appear.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Benedetti, Julia. “Introduction to hypersensitivity and reactive skin disorders”. Merckmanuals. Merck & Co., 2022, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/dermatologic-disorders/hypersensitivity-and-reactive-skin-disorders/introduction-to-hypersensitivity-and-reactive-skin-disorders
[1]Marwa, K., and N. P. Kondamudi. "Type IV Hypersensitivity Reaction. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing, 2021.
[2]Vaillant, Angel A. Justiz, Rishik Vashisht, and Patrick M. Zito. "Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions." StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing, 2022.
[3]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAELaiu6tAo-hypersensitivity/
[4]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAC3SocXsPI-doctor-testing-allergy-reaction/
