Difference Between Johnson & Johnson and AstraZeneca
Thousands of volunteers from diverse backgrounds enrolled in the clinical trials in 2020 for COVID-19 vaccine development. Thanks to the commitment of those individuals along with the sheer will and dedication of the scientists who have been working days and nights looking for a cure for this infectious disease, we now have a couple of vaccine candidates which are already under mass circulation. A vaccine is now our only ray of hope in addressing the global health crisis. The development of COVID-19 vaccines was only possible through the hard work of individuals and those who volunteered for the clinical trials. Now that we have a few vaccine candidates, including the Oxford University’s AstraZeneca vaccine and the Johnson & Johnson/Janssen vaccine, the question is which one’s more effective and which one should you take?

What is Johnson & Johnson Vaccine?
The Johnson & Johnson vaccine, developed by Janssen Pharmaceutical – a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson, was approved for emergency use on 27 Feb. 2021, after successful clinical trials suggested that the most recent vaccine candidate is very effective against coronavirus-related hospitalizations and deaths. Unlike other vaccine candidates, the Johnson & Johnson (Janssen) vaccine is the only single-shot vaccine out there to be approved for EUA by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The Janssen vaccine uses the company’s proprietary AdVac vaccine platform for vaccine development – the same technology which was used for the development of Ebola vaccine.
The Janssen vaccine was developed with a non-replicating adenovirus vector, which is a completely harmless virus that causes the common cold. The virus has been genetically modified to carry a portion of the virus called spike proteins that causes the coronavirus infection in humans. Our body then creates the spike proteins by itself which prompt our cells to trigger an automatic immune response against that spike protein, which finally makes us immune to coronavirus infection by creating antibodies. The vaccine is also safe to store and transport so it’s likely to be available in rural areas and hospitals with limited ultra cold freezer capacity.
What is AstraZeneca Vaccine?
The AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine, codenamed AZD1222, is developed by the University of Oxford in partnership with the global pharmaceutical company, AstraZeneca, and sold under different names, such as Covishield and Vaxzevria among others. This is one of the leading COVID-19 vaccine candidates and one of the fewer vaccines to be approved for mass inoculation in order to put a halt on the increasing caseload of infections. Although, the vaccine had shown promising results in the phase III of clinical trials, as a result of which it was approved for EUA, many patients after getting vaccinated with the first dose started showing signs of blood clots.
The question still remains, is it safe to take the AstraZeneca vaccine, considering the European medical agencies have already confirmed that the vaccine is safe to use and that its benefits outweighs the risks associated with the vaccine. They further suggested that the risks associated with the vaccine are very rare and out of millions of people that took the vaccine, only about 30 had rare types of blood clots. Many health care officials and experts on the field have also confirmed that there is no reason to panic and a lot of investigation has been going on to determine the exact reason of the blood clots.
Difference between Johnson & Johnson Vaccine and AstraZeneca Vaccine
Type of Johnson & Johnson Vaccine and AstraZeneca Vaccine
– Both AstraZeneca and Janssen COVID-19 vaccine candidates use the same technology for their vaccine development, a non-replicating virus called the adenovirus which causes common cold in chimpanzees and contains the genetic code of the SARS-CoV-2 virus spike protein – the virus that causes the coronavirus disease. This is actually a weakened virus that is not capable enough to cause any harm to us.
Both are DNA vaccines but deliver the same results as the mRNA vaccines from Pfizer and Moderna – after the vaccine, our body starts to build a strong immune response against the spike protein without directly exposing our body to the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which ultimately makes us immune to the COVID-19 infection.
Efficacy of Johnson & Johnson Vaccine and AstraZeneca Vaccine
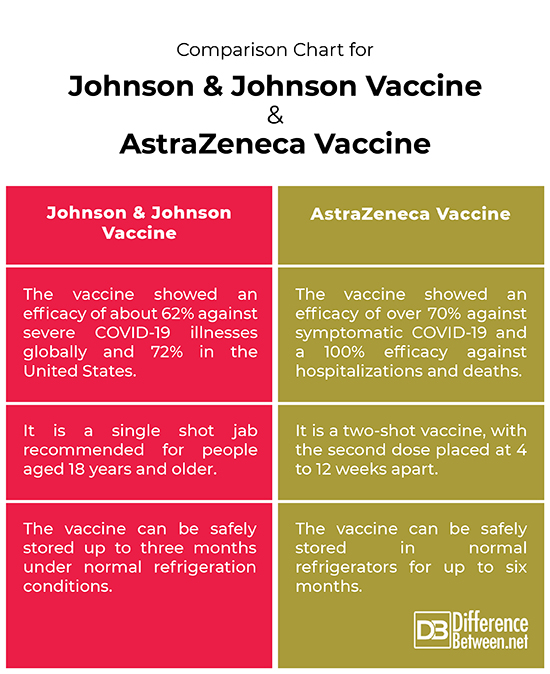
– If you just look at the numbers and the statistics, you can see that statistically they are not so different after all, but considering both the vaccines were tested and developed during different time periods in different populations, they are considered highly effective. That being said, AstraZeneca vaccine is completely effective against severe COVID-19 related illnesses and hospitalizations, demonstrating an efficacy of over 70% against symptomatic COVID-19 and a 100% efficacy against hospitalizations and deaths.
The Janssen vaccine showed an efficacy of about 62% against severe COVID-19 illnesses based on the data of clinical trials and 72% in the United States. But considering the clinical trials of the AstraZeneca vaccine were done before more infectious variants of the virus became widespread, the numbers may not mean anything since the Janssen vaccine trials were conducted under more stringent conditions.
Dose of Johnson & Johnson Vaccine and AstraZeneca Vaccine
– The AstraZeneca is a two-shot vaccine administered as an intramuscular injection, 0.5 ml each and the second dose is placed at 4 to 12 weeks apart. It takes almost 2 weeks to kick off and develop protection against the infection. Unlike AstraZeneca, the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine is a single shot jab recommended for people aged 18 years and older.
Storage of Johnson & Johnson Vaccine and AstraZeneca Vaccine
– Both the vaccines are the easiest to transport so far, since they do not require ultra cold freezers for storage. Both the vaccines can be stored, transported and handled at normal refrigerated conditions. While the AstraZeneca vaccine can be safely stored in normal refrigerators for up to six months, the Janssen vaccine is estimated to remain stable at -20°C for as long as two years and a maximum of three months under normal refrigeration conditions.
Comparison chart for Johnson & Johnson Vaccine and AstraZeneca Vaccine
Summary
Both AstraZeneca and Janssen vaccines are based on the same adenovirus viral vector technology that uses a weakened version of a virus that causes common cold in chimpanzees and contains the genetic code of the SARS-CoV-2 virus spike protein, which is completely harmless. Both the vaccines are fairly effective against severe COVID-19 related illnesses and hospitalizations, but considering the Janssen vaccine trials were conducted under more stringent conditions, the Janssen vaccine could be a leading vaccine candidate. However, the use of both the vaccines has been suspended in the United States following reports of rare blood clot issues in people who have been vaccinated with the doses.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Rabadan, Raul. Understanding Coronavirus. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2020. Print
[1]Edwards, Kathryn M., et al. The Covid-19 Vaccine Guide: The Quest for Implementation of Safe and Effective Vaccinations. New York, United States: Simon and Schuster, 2021. Print
[2]Saxena, Shailendra K. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapeutics. Berlin, Germany: Springer Nature, 2020. Print
[3]Dr. Benarroch, Amanda. “Scientists exploring possible link between Johnson & Johnson, AstraZeneca vaccine blood clot issues.” ABC News, ABC News Internet Ventures, 17 April 2021, abcnews.go.com/Health/scientists-exploring-link-johnson-johnson-astrazeneca-blood-clot/story?id=77093834. Accessed 20 April 2021.
[4]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/65535/50714724757_cd08941b3f_b.jpg
[5]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/65535/51001567821_92abbb66db_b.jpg
